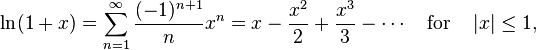SDL绘制
要在SDL的窗口中绘图 需要先获得 SDL_Surface
SDL提供了SDL_GetWindowSurface(SDL_Window *)来获得客户区的SDL_Surface1
2
3
4
5
6SDL_Window *win=SDL_CreateWindow("HelloWorld",
SDL_WINDOWPOS_CENTERED,
SDL_WINDOWPOS_CENTERED,
WIDTH,HEIGHT,
SDL_WINDOW_SHOWN);
SDL_Surface *screen=SDL_GetWindowsSurface(win);
获得了SDL_Surface之后 我们有两种方法可以绘制客户区
利用SDL提供的函数
SDL提供了一些函数来方便绘制
例如SDL_FillRect(SDL_Surface *s,SDL_Rect *r,uint32_t color)
其中 第三个参数是颜色值 按照ARGB顺序排列 每个值为八位
我们可以利用这个函数将客户区涂成白色
1 | SDL_Rect r={0,0,WIDTH,HEIGHT}; |
手动绘制
SDL_Surface是一个结构体,其定义如下
1 | typedef struct SDL_Surface |
我们需要关注其中的 w,h 和pixels
w h 分别是宽度和高度
而pixels是一个指向一块内存的指针 此处定义为void *实际使用时可转换为uint32_t *
他对应着屏幕上任意一点处的像素的颜色值 颜色定义为ARGB
而(x,y)处的的像素获取方式为(uint32_t *)pixels[x*w+y]
我们通过手动绘制来画一个100x100的方块 放置于(0,0)处1
2
3
4
5
6uint32_t *p=(uint32_t *)screen->pixels;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
for(int j=0;j<100;j++){
p[i*screen->w+j]=0xff0000ff;//ARGB Blue 100%
}
}
SDL2事件循环
SDL为事件处理提供了灵活的API,当收到来自设备的事件时,SDL会将其存入事件队列等待取出
在程序中,应当有一个循环来处理这些事件,每次循环时应从中取出事件并处理它
SDL 提供了 SDL_PollEvent(SDL_Event *)函数来提供取出事件的功能
如果对列中还有事件 则会取出事件存入SDL_Event类型的变量中 并返回一个非零值 否则返回零
轮询事件后,您可以在逻辑链中响应它。
为了方便阅读 通常会将循环抽出写成一个函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13void eventloop(){
SDL_Event e;
while(1){
while(SDL_PollEvent(&e)){
switch(e.type){
case SDL_QUIT:
return;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
代码