Mininet
1. Mininet 基本使用
Mininet指令
net
查看拓扑链接情况
xterm
xterm [hosts]
打开对应主机终端
pingall
测试所有设备联通性
在对应主机执行指令
[host] {command}
iperf指令
1 | iperf |
2. 链路性能参数设置及iperf数据绘图
链路性能设置
mn --link=tc,loss=[loss_rate],bw=[band_width],delay='[delay]'
loss -> 每条链路的丢包率
bw -> 链路带宽
delay -> 每条链路的延迟
iperf结果绘图
在服务器端使用 iperf -s -i 1 | tee tcp.txt
将结果通过管道存放到文件
效果如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on TCP port 5001
TCP window size: 85.3 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 14] local 10.0.0.2 port 5001 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 60150
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 14] 0.0- 1.0 sec 1.08 MBytes 9.09 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 1.0- 2.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.56 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 2.0- 3.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 3.0- 4.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.56 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 4.0- 5.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 5.0- 6.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 6.0- 7.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.56 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 7.0- 8.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 8.0- 9.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.55 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 9.0-10.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.58 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 10.0-11.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 11.0-12.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.55 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 12.0-13.0 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.58 Mbits/sec
[ 14] 0.0-13.1 sec 14.9 MBytes 9.53 Mbits/sec
然后 使用
1 | cat tcp.txt | grep sec | head -n 10 | tr "-" " " | awk '{print $4,$8} > a' |
其中
cat tcp.txt读取文件并显示grep sec会标记出含有sec的列head -n 10取出前十行tr "-" " "会将-替换为空格awk '{print $4,$8}'会取出第四列和第八列
效果如下1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
101.0 9.09
2.0 9.56
3.0 9.57
4.0 9.56
5.0 9.57
6.0 9.57
7.0 9.56
8.0 9.57
9.0 9.55
10.0 9.58
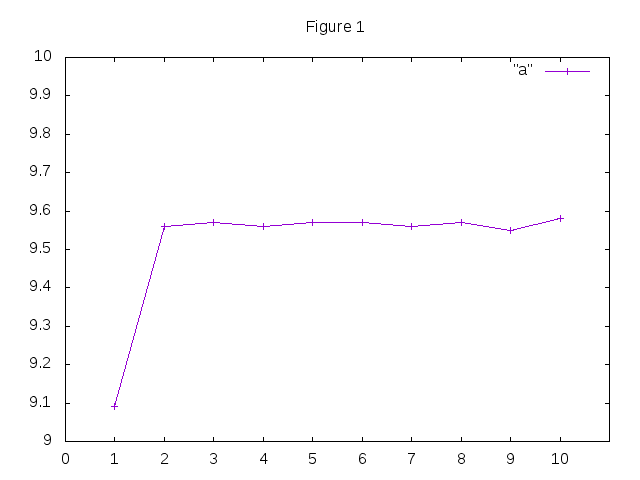
然后我们使用gnuplot绘图
- 输入
gnuplot回车 进入gnuplot - 输入
plot "a" title "tcp" with linespoints绘图,"a"为文件名,title "tcp"设置标题,with linespoints设置为带点直线 set xrange[0:10]和set yrange[0:10]设置x、y轴范围 0 ~ 10set xtics 0,1,10和set ytics 0,1,10设置x、y轴刻度 0开始 10结束 1步进set xlabel "time(sec)"和set ylabel "Throughput(Mbps)"设置x、y轴标记文字set title "Tcp"设置图标标题为Tcpset terminal gif设置保存格式为gifset output "a.gif"设置保存的文件名为a.gifreplot修改设置后重绘或者可以保存文件
3. 使用Mininet脚本创建简单网络拓扑
1. 最简单的路由结构
h1 —— h2
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
2. 含一个路由的结构
h1 —— r —— h21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17#!/usr/bin/env python
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.link import Link,TCLink
if '__main__' == __name__:
net = Mininet(link=TCLink)
h1 = net.addHost('h1')
h2 = net.addHost('h2')
# 这是作为路由器的设备
r = net.addHost('r')
# 建立到路由的链接
Link(h1,r)
Link(h2,r)
net.build()
CLI(net)
net.stop()
此时网络拓扑结构如下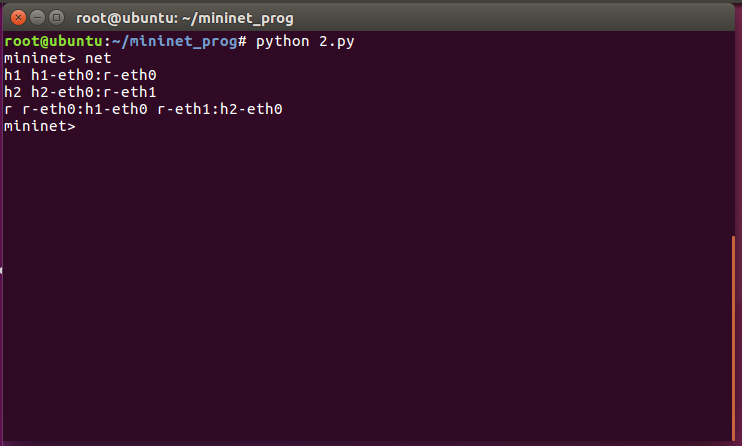
此时h1和h2是不连通的 需要配置路由使其联通
规划如下:
- h1 使用 192.168.1.1/24
- h2 使用 192.168.2.1/24
- h1 使用 192.168.1.254 与 r 连接
- h2 使用 192.168.2.254 与 r 连接
步骤如下: - h1 使用 ifconfig h1-eth0 0 清空分配的地址
- h1 使用 ifconfig h1-eth0 192.168.1.1/24 分配地址
- h2 使用 ifconfig h2-eth0 0 清空分配的地址
- h2 使用 ifconfig h2-eth0 192.168.2.1/24 分配地址
- h1 使用 ip route add default via 192.168.1.254 设定默认路由
- h2 使用 ip route add default via 192.168.2.254 设定默认路由
- r 使用 ifconfig r-eth0 0 清空分配的地址
- r 使用 ifconfig r-eth0 192.168.1.254/24 分配地址
- r 使用 ifconfig r-eth1 0 清空分配的地址
- r 使用 ifconfig r-eth1 192.168.2.254/24 分配地址
此时两台host已经互通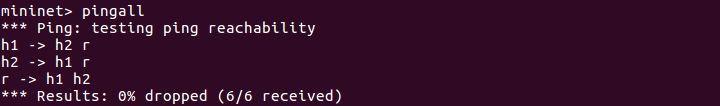
3. 使用脚本自动建立路由
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
4. 使用Mininet脚本创建复杂网络拓扑
1. 两个路由器
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
拓扑结构如下:
h1 h1-eth0:r1-eth0
h2 h2-eth0:r2-eth0
r1 r1-eth0:h1-eth0 r1-eth1:r2-eth1
r2 r2-eth0:h2-eth0 r2-eth1:r1-eth1
2.NAT地址转换
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
其中 iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o r1-eth1 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j MASQUERADE 起到了启动NAT的作用-t指定了表名为NAT-A指定了在POSTROUTING末尾插入规则-o匹配流出网卡为r1-eth1-s匹配源地址为192.168.1.0/24网段-j使用MASQUERADE选项进行地址伪装 可以自动匹配当前流出网卡的ip地址无需手动指定
5. Mininet中如何创建bridge
1.简单的桥接
1 | br1: mybr |
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
2.两个网桥
1 | br1: |
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
3. 两网桥间互通
通过添加路由器r1 让流量穿过r1 使两网桥互通1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 r1
|
|
+-------+------+
br1: | |
+---|--------------|----+
| mybr1 mybr2 |
+---|--------------|----+
| |
+--+--+ +--+--+
| | | |
h1 h2 h3 h4
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
- 注:
brctl用于管理网桥 在bridge-utils包下brctl addbr <br_name>添加名为br_name的网桥brctl addif <br_name> <if_name>添加名为if_name的接口到br_name的网桥- 网桥不会自动up 需要
ifconfig <br_name> up
6. Mininet VLAN 配置
虚拟局域网(VLAN)是一组逻辑上的设备和用户,这些设备和用户并不受物理位置的限制,可以根据功能、部门及应用等因素将它们组织起来,相互之间的通信就好像它们在同一个网段中一样,由此得名虚拟局域网
通过添加vlan 减少一个网桥
1 | r1 |
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python |
数据包在穿过网桥送往路由器时会被打上一个特殊标签
从vlan.10发往router时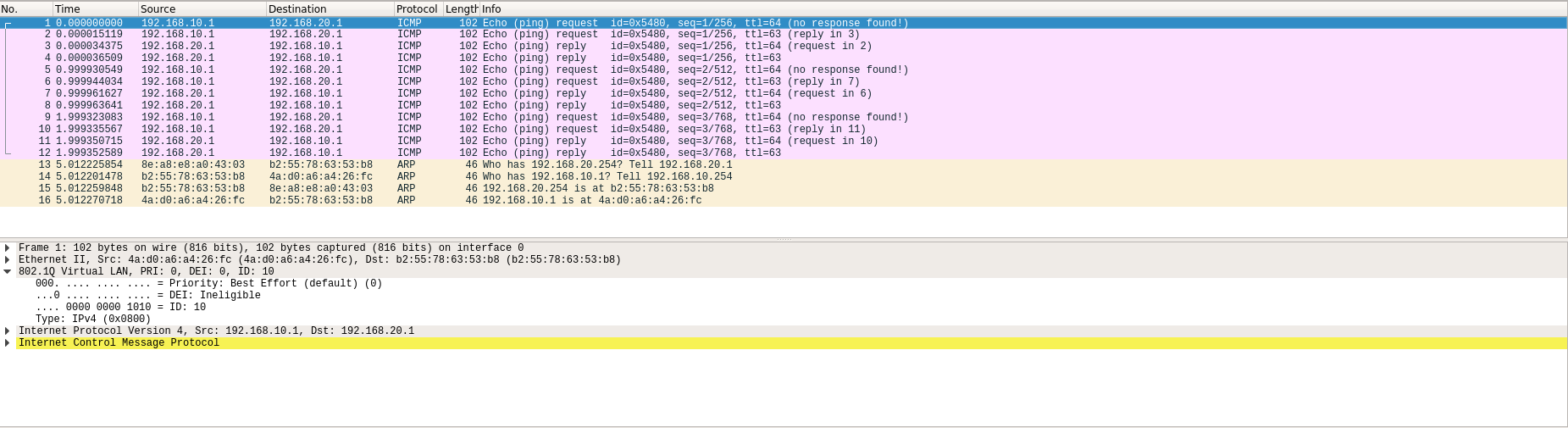
从vlan.20发往router时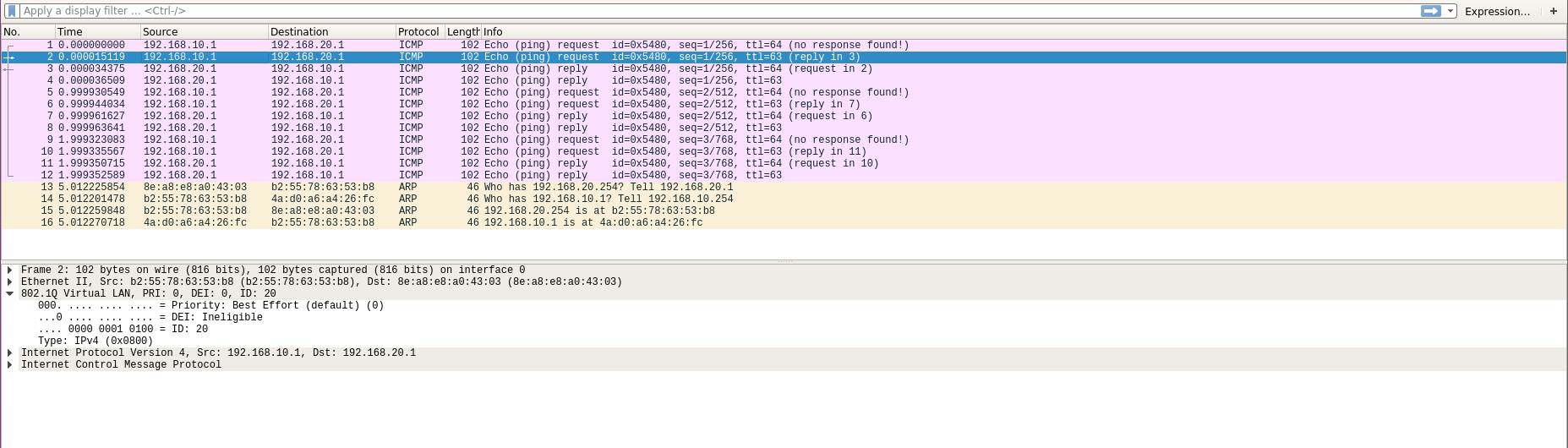
7. Mininet中OVS的基本操作
OVS 基本指令
1. ovs-ofctl show
显示OVS交换机的基本信息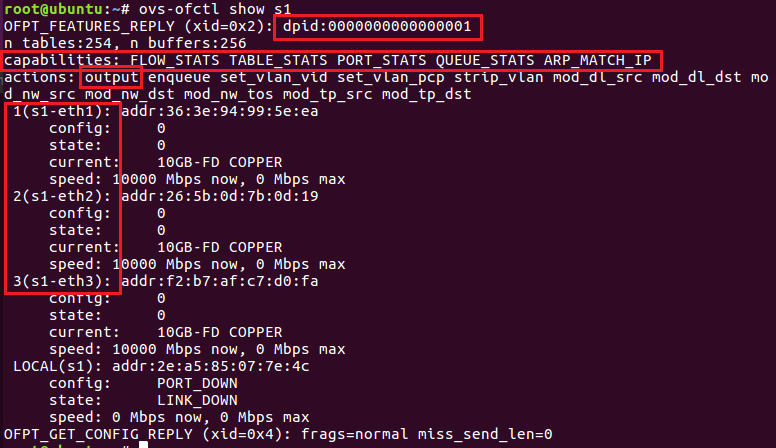
dpid -> OVS 交换机的唯一ID
capabilities -> 交换机具有的能力
actions -> 交换机可执行的操作 例如:
- output 转发输出
- mod_nw_dst 修改目的地址
等等
1,2,3 为该交换机具有的端口及其端口号
2. ovs-ofctl add-flow
添加交换机的规则
例如 ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=1,actions:output:2
3. ovs-ofctl del-flows
删除该交换机上所有规则
4. ovs-ofctl del-flows
删除该交换机上匹配的规则
例如 ovs-ofctl del-flows s1 in_port=1
该指令将删除in_port=1对应的规则
5. ovs-ofctl dump-flows
显示该交换机上所有规则
OVS 操作
1.两台主机的简单拓扑
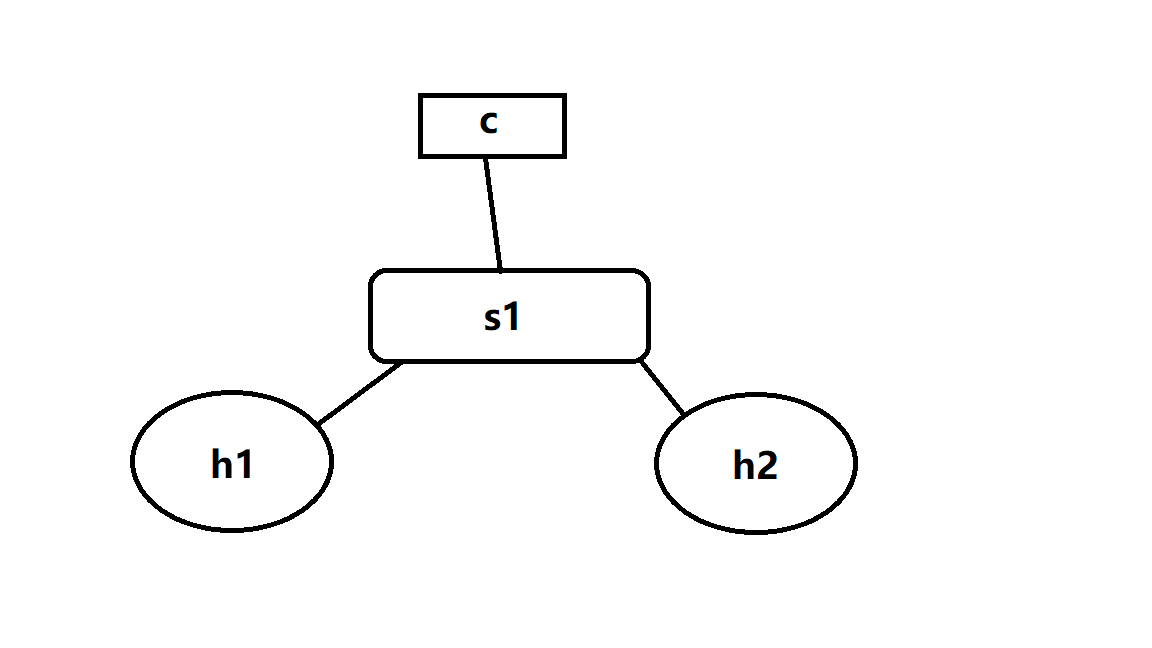
通过mininet --topo sigle,2
建立拥有1台switch 两台host的拓扑
首先 使用ps -aux | grep controller
获得controller的PID 然后使用 kill -9 <PID> 杀掉controller
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=1,actions=output:2将1口数据包转发到2口ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=2,actions=output:1将2口数据包转发到1口
此时 两台主机可以ping通
2.三台主机的拓扑
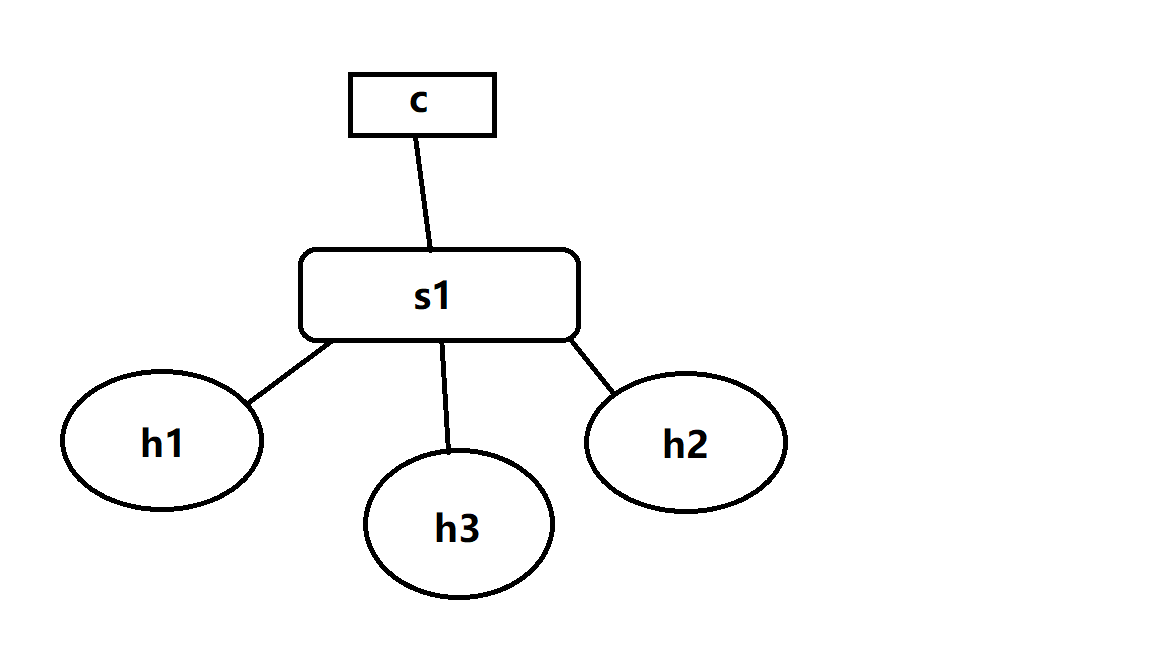
通过mininet --topo sigle,3
建立拥有1台switch 三台host的拓扑
首先 使用ps -aux | grep controller
获得controller的PID 然后使用 kill -9 <PID> 杀掉controller
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=1,arp,actions=output:flood将1口的arp数据包泛洪ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=2,arp,actions=output:flood将2口的arp数据包泛洪ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 in_port=3,arp,actions=output:flood将3口的arp数据包泛洪ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1将发往10.0.0.1的数据转发到1口ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2将发往10.0.0.2的数据转发到2口ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.3,actions=output:3将发往10.0.0.3的数据转发到3口
此时 三台主机可以互相ping通
8. Mininet中SSH服务配置
- 使用
netstat -tunlp | grep 22查看sshd是否已经运行 - 使用
which sshd获得sshd位置 - 使用完整路径启动sshd(不能使用
systemctl或者service)
9. containernet介绍
1. 切换到containernet环境
1 | cd /home/user/containernet |
2. 创建需要的docker镜像
1 | docker pull ubuntu:16.04 |
在docker环境内 安装需要的软件 并创建用户1
2
3apt update
apt install net-tools iputils-ping iproute openssh-server
adduser user
完成后 新建一个终端 使用docker ps查看正在运行的镜像 获得container-id
然后使用docker commit <container-id> <name:tag>
将当前container保存为image
本次创建了两个镜像 ubuntu:sshd1 ubuntu:sshd2
然后编写脚本1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28#!/usr/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Controller
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.link import TCLink
from mininet.log import info, setLogLevel
setLogLevel('info')
net = Containernet(controller=Controller)
info('*** Adding controller ***')
net.addController('c0')
info('*** Adding docker containers ***')
h1 = net.addHost('h1', ip='10.0.0.250/24')
d1 = net.addDocker('d1', ip='10.0.0.251/24', dimage='ubuntu:sshd1')
d2 = net.addDocker('d2', ip='10.0.0.252/24', dimage='ubuntu:sshd2')
info('*** Adding switches ***')
s1 = net.addSwitch('s1')
info('*** Creating links ***')
net.addLink(h1, s1)
net.addLink(d1, s1)
net.addLink(d2, s1)
info('*** Starting network ***')
net.start()
info('*** Runing CLI ***')
CLI(net)
info('*** Stopping network ***')
net.stop()
运行脚本后 可以使用docker ps查看到正在运行的容器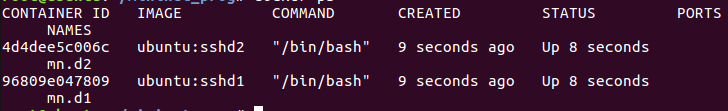
可以使用docker exec -it mn.d1 bash进入d1主机 然后使用ifconfig检查IP是否设定正确
最后使用/etc/init.d/ssh start开启ssh服务
对d2执行相同操作即可
然后在mininet控制台 使用xterm h1 开启h1的终端
输入ssh user@10.0.0.251可以远程登录到d1主机
输入ssh user@10.0.0.252可以远程登录到d2主机
10. Mininet 应用-如何建立反向代理
前置准备
- 安装golang
- 从GitHub克隆frp 并编译出可执行文件
拓扑结构
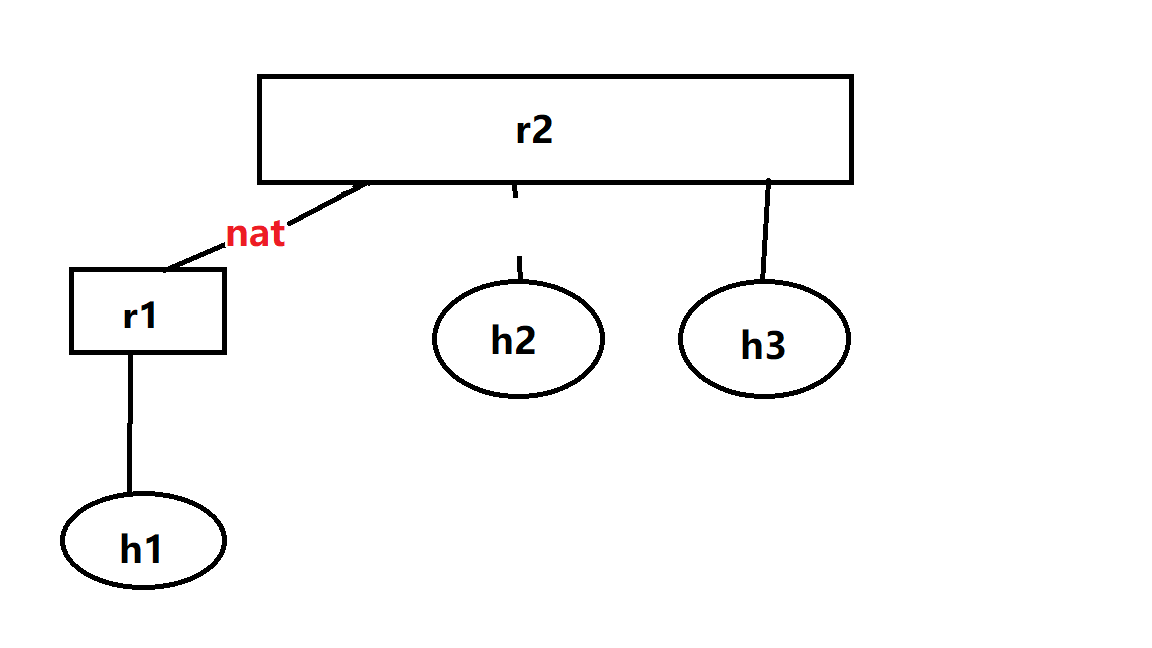
使用的脚本
1 | #!/usr/bin/python |
操作步骤
- 运行脚本 建立拓扑结构
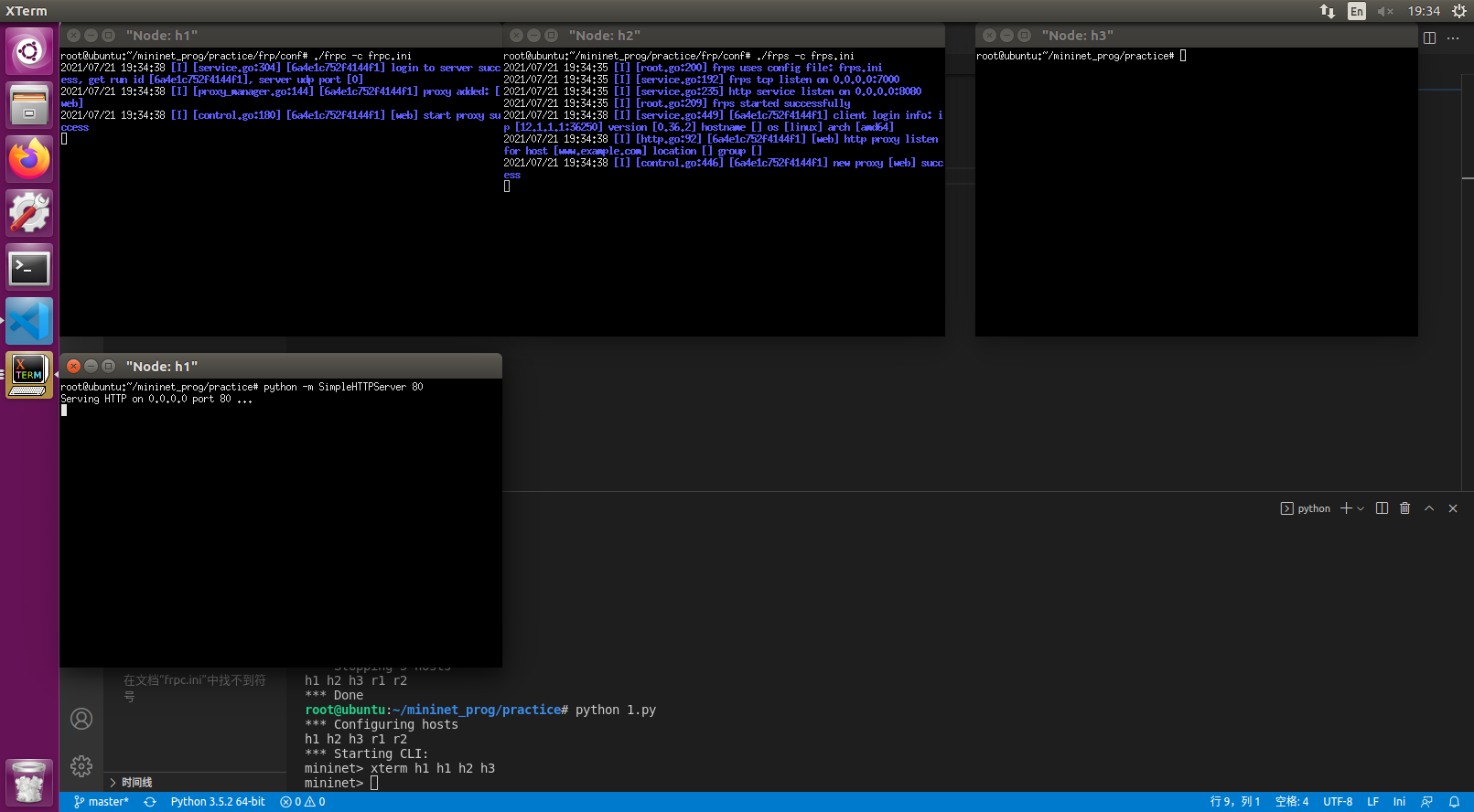
xterm h1 h1 h2 h3- 在其中一个h1终端上 执行
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 - 在h2上编辑frps.ini 内容如下
frps.ini 1
2
3[common]
bind_port = 7000
vhost_http_port = 8080 - h2运行
frps -c frps.ini - h1另一台终端编辑frpc.ini
frpc.ini 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8[common]
server_addr = 1.1.1.1
server_port = 7000
[web]
type = http
local_port = 80
custom_domains = www.example.com - 在h1运行
frpc -c frpc.ini - 在
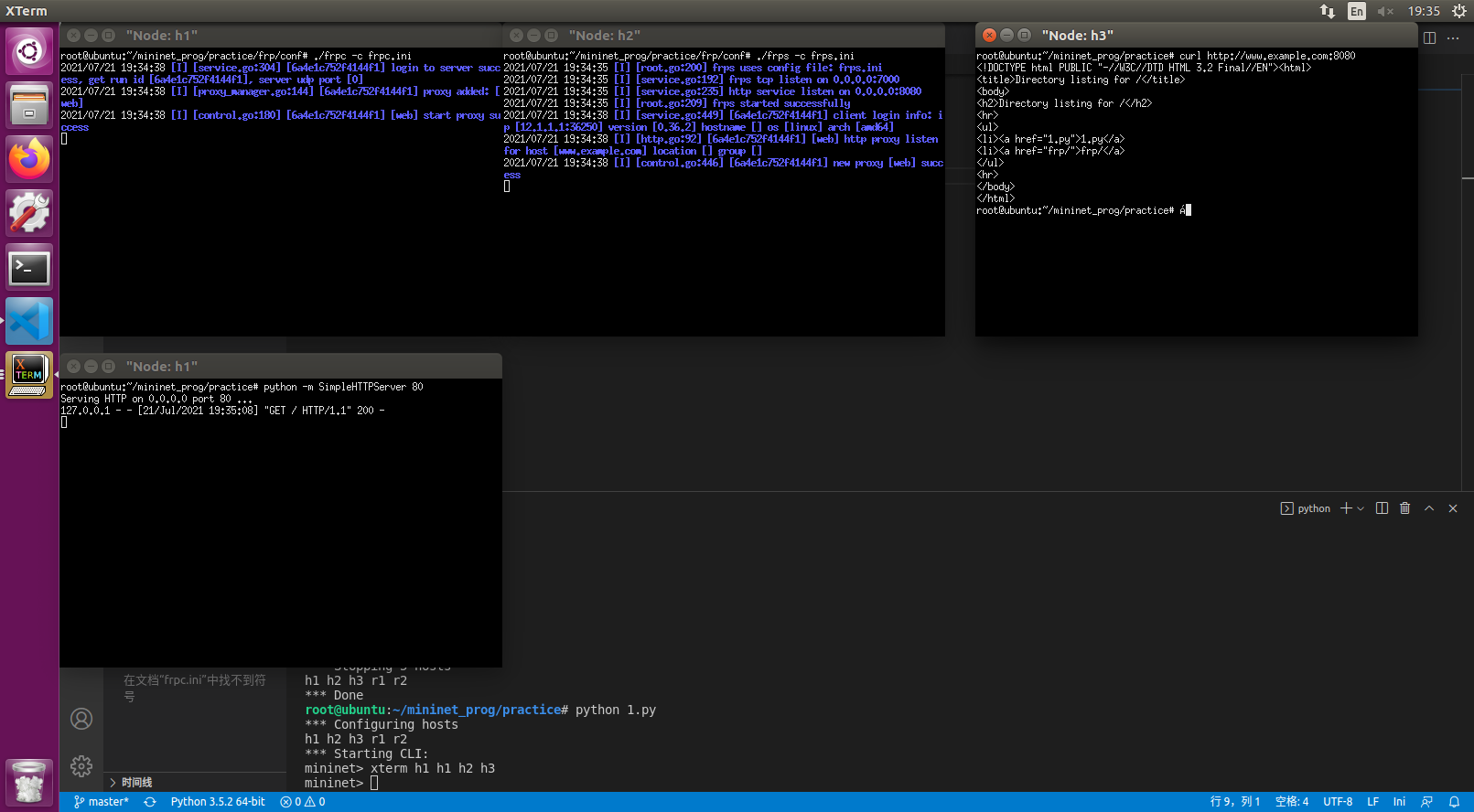
/etc/hosts添加1.1.1.1 www.example.com - 在h3可以使用
curl www.example.com:8080取得网页
11. Mininet 应用-如何建立SSH隧道
本节将介绍ssh的三种转发方式
本节使用containernet
1. Local Forwarding
简单的点对点拓扑
拓扑结构如下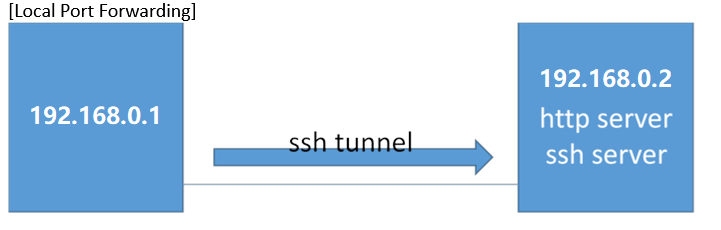
目标:访问在192.168.0.2上的http页面 但是通过ssh加密
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30#!/user/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Docker
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel,info
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link
def topology():
net=Containernet()
info("Adding hosts")
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='192.168.0.1/24')
d1=net.addDocker('d1',ip='192.168.0.2/24',dimage='smallko/php-apache-dev:v10')
info("Create links")
net.addLink(h1,d1)
info("Starting network")
net.start()
d1.cmd("/etc/init.d/ssh start")
info("Running CLI")
CLI(net)
info("Atopping network")
net.stop()
if __name__=="__main__":
setLogLevel('info')
topology()
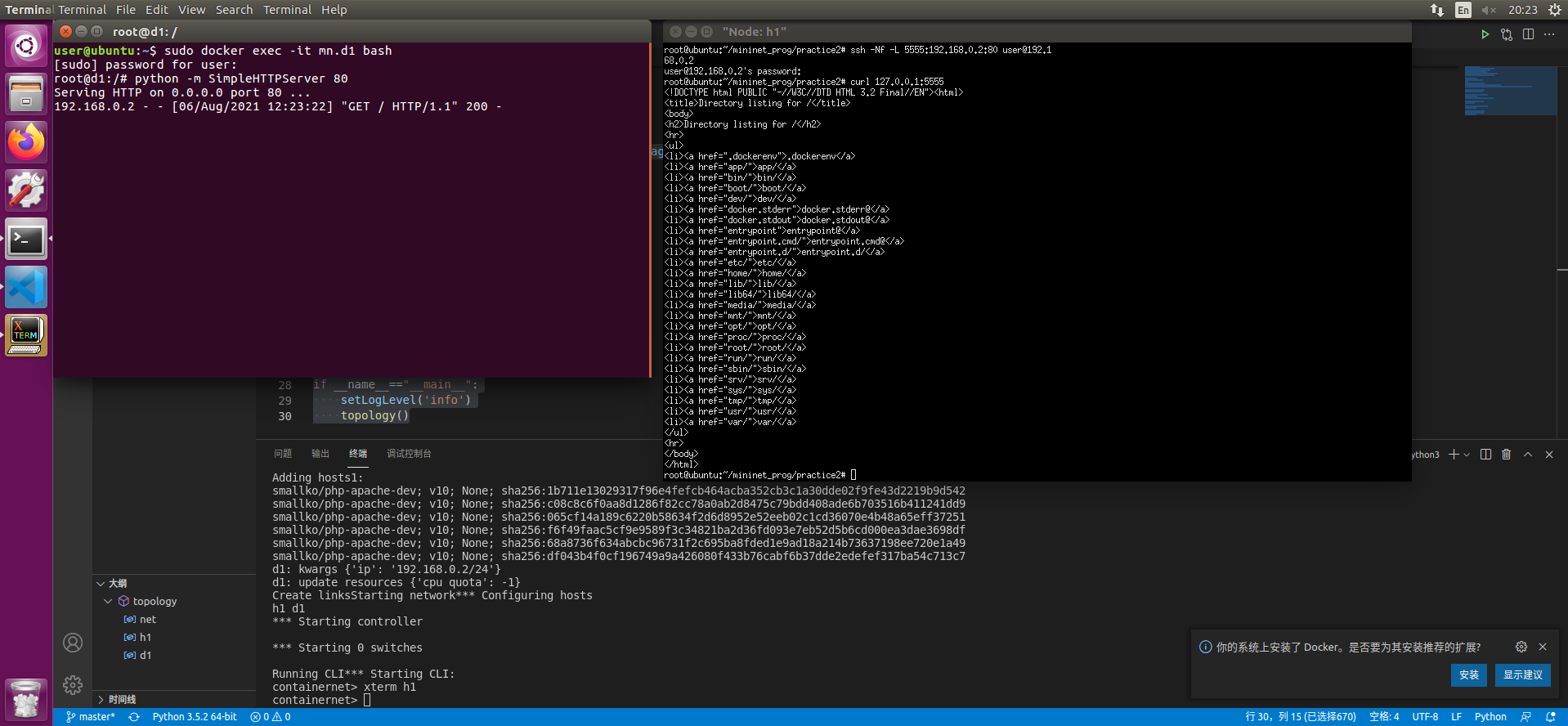
- 打开一个终端 使用
sudo docker exec -it mn.d1 bash打开d1的终端 - 在其中输入
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 - 在CLI中输入xterm h1
- 在h1终端中使用
ssh -Nf -L 5555:192.168.0.2:80 user@192.168.0.2 - 输入密码建立链接 此时可以使用
curl 127.0.0.1:5555获得远端服务器的内容
带有中间主机的点对点访问
拓扑结构如下
目标:通过192.168.0.2访问在192.168.0.3上的http页面 但是通过ssh加密
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42#!/user/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Docker
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel,info
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link
def topology():
net=Containernet()
info("Adding hosts")
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='192.168.0.1/24')
d1=net.addDocker('d1',ip='192.168.0.2/24',dimage='smallko/php-apache-dev:v10')
h2=net.addHost('h2',ip='192.168.0.3/24')
br1=net.addHost('br1')
info("Create links")
net.addLink(h1,br1)
net.addLink(d1,br1)
net.addLink(h2,br1)
info("Starting network")
net.start()
d1.cmd("/etc/init.d/ssh start")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth0 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth1 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth2 0")
br1.cmd("brctl addbr br1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth0")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth2")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1 up")
info("Running CLI")
CLI(net)
info("Atopping network")
net.stop()
if __name__=="__main__":
setLogLevel('info')
topology()
- 在CLI中输入xterm h1 h2
- 在h2终端输入
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 - 在h1终端中使用
ssh -Nf -L 5555:192.168.0.3:80 user@192.168.0.2 - 输入密码建立链接 此时可以使用
curl 127.0.0.1:5555获得远端服务器的内容
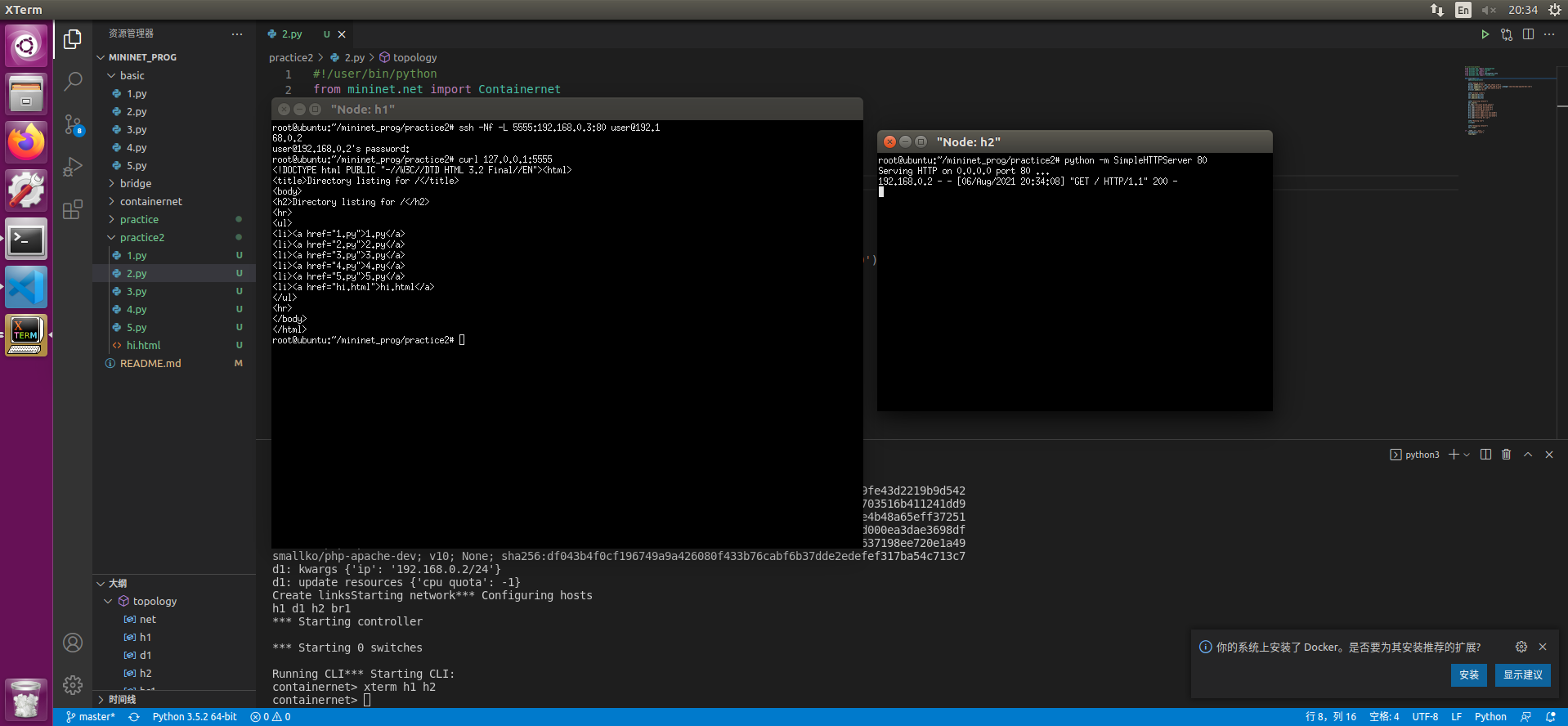
2. Local Forwarding
从外网穿透访问内网服务器
拓扑结构如下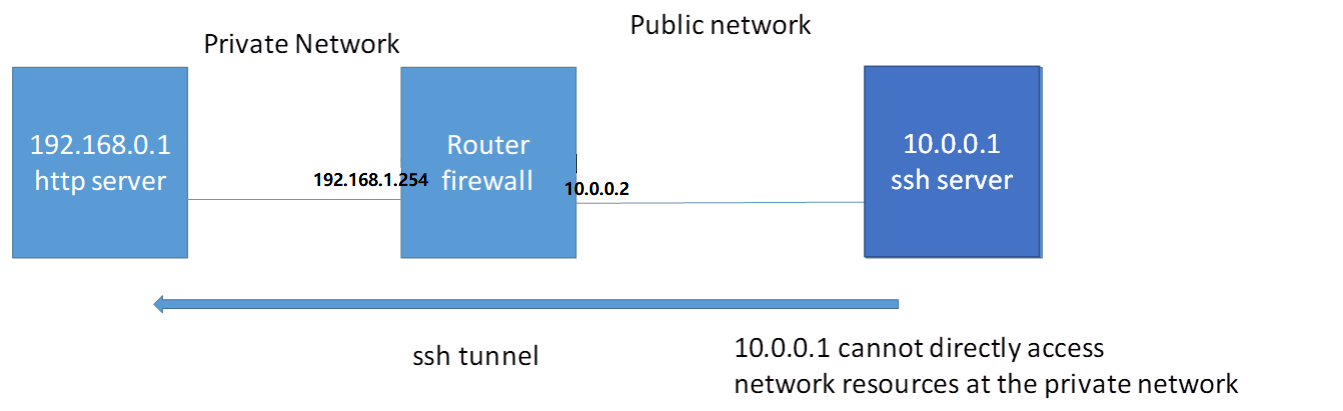
目标: 由于路由器的NAT public network 不能直接存取 private network 的内容 使用ssh远程穿透路由器以达到存取内网内容的目的
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37#!/user/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Docker
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel,info
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link
def topology():
net=Containernet()
info("Adding hosts")
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='192.168.0.1/24')
r1=net.addHost('r1',ip='192.168.0.254/24')
d1=net.addDocker('d1',ip='10.0.0.1/24',dimage='smallko/php-apache-dev:v10')
info("Create links")
net.addLink(h1,r1)
net.addLink(r1,d1)
info("Starting network")
net.start()
d1.cmd("/etc/init.d/ssh start")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 0")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 10.0.0.2/24")
r1.cmd("echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward")
r1.cmd("iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -o r1-eth1 -j MASQUERADE")
h1.cmd("ip route add default via 192.168.0.254")
info("Running CLI")
CLI(net)
info("Atopping network")
net.stop()
if __name__=="__main__":
setLogLevel('info')
topology()
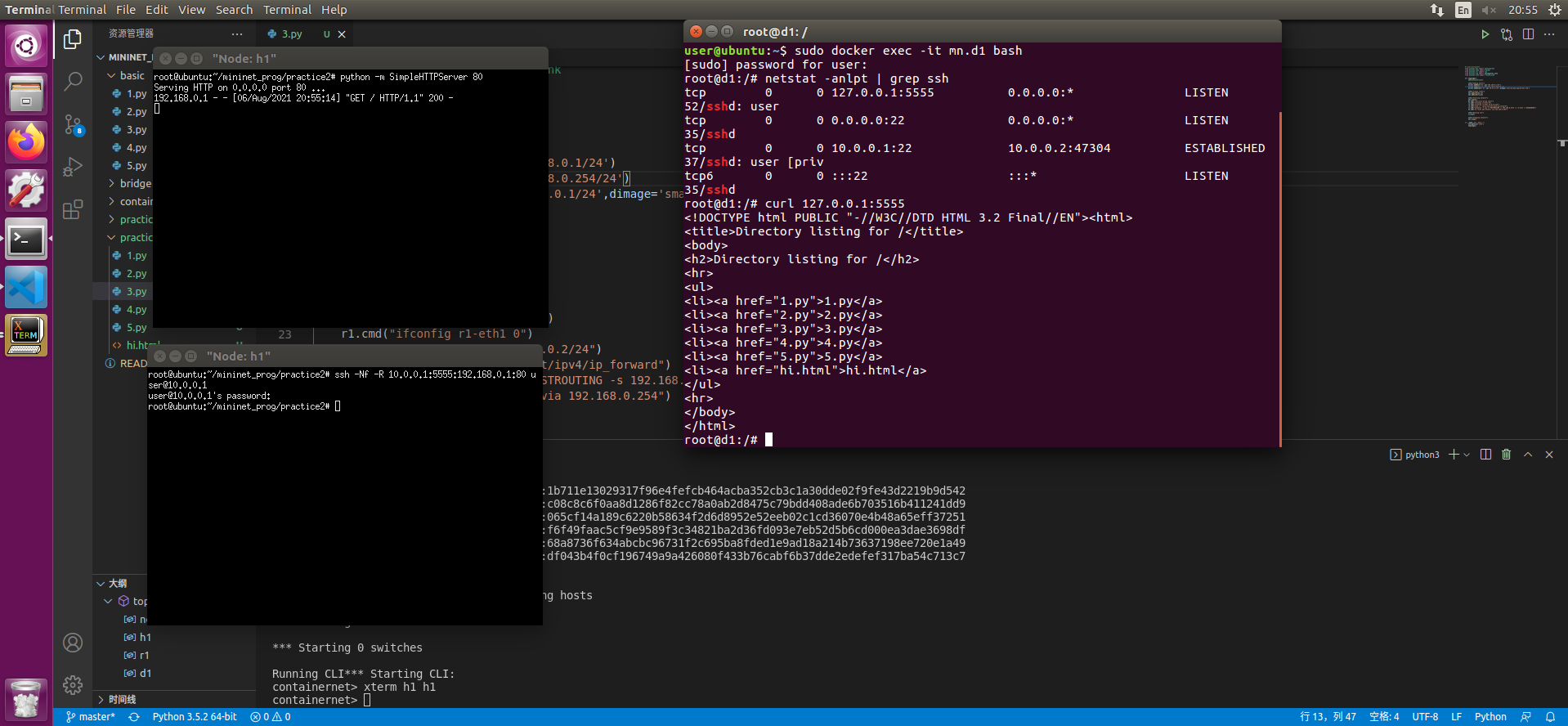
- 在CLI中输入xterm h1 h1
- 在一个h1终端输入
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 - 在另一个h1终端中使用
ssh -Nf -R 10.0.0.1:5555:192.168.0.1:80 user@10.0.0.1输入密码 - 开启一个终端 输入
sudo docker exec -it mn.d1 bash - 使用
curl 127.0.0.1:5555即可访问192.168.0.1的内容
更复杂的情况
拓扑结构如下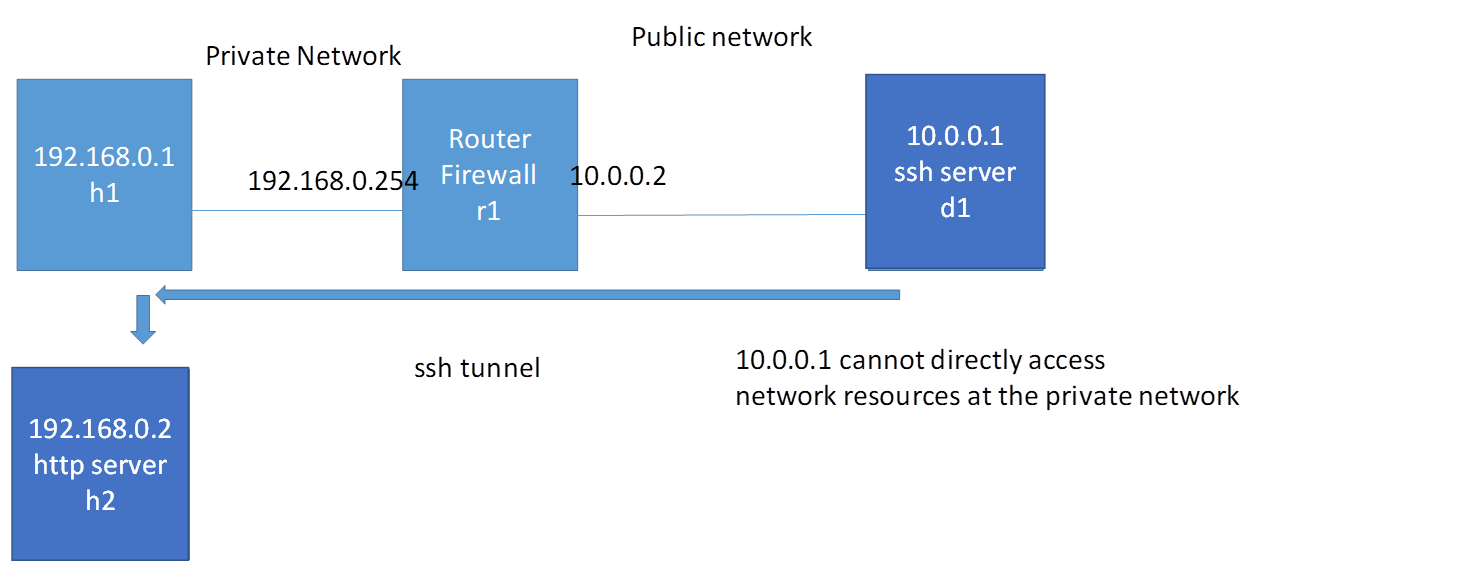
目标: 存取内网的另一台主机
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49#!/user/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Docker
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel,info
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link
def topology():
net=Containernet()
info("Adding hosts")
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='192.168.0.1/24')
h2=net.addHost('h2',ip='192.168.0.2/24')
br1=net.addHost('br1')
r1=net.addHost('r1',ip='192.168.0.254/24')
d1=net.addDocker('d1',ip='10.0.0.1/24',dimage='smallko/php-apache-dev:v10')
info("Create links")
net.addLink(h1,br1)
net.addLink(h2,br1)
net.addLink(r1,br1)
net.addLink(r1,d1)
info("Starting network")
net.start()
d1.cmd("/etc/init.d/ssh start")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 0")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 10.0.0.2/24")
r1.cmd("echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward")
r1.cmd("iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -o r1-eth1 -j MASQUERADE")
h1.cmd("ip route add default via 192.168.0.254")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth0 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth1 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth2 0")
br1.cmd("brctl addbr br1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth0")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth2")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1 up")
info("Running CLI")
CLI(net)
info("Atopping network")
net.stop()
if __name__=="__main__":
setLogLevel('info')
topology()
- 在CLI中输入xterm h1 h2
- 在h2终端输入
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 - 在h1终端中使用
ssh -Nf -R 10.0.0.1:5555:192.168.0.2:80 user@10.0.0.1输入密码 - 开启一个终端 输入
sudo docker exec -it mn.d1 bash - 使用
curl 127.0.0.1:5555即可访问192.168.0.1的内容
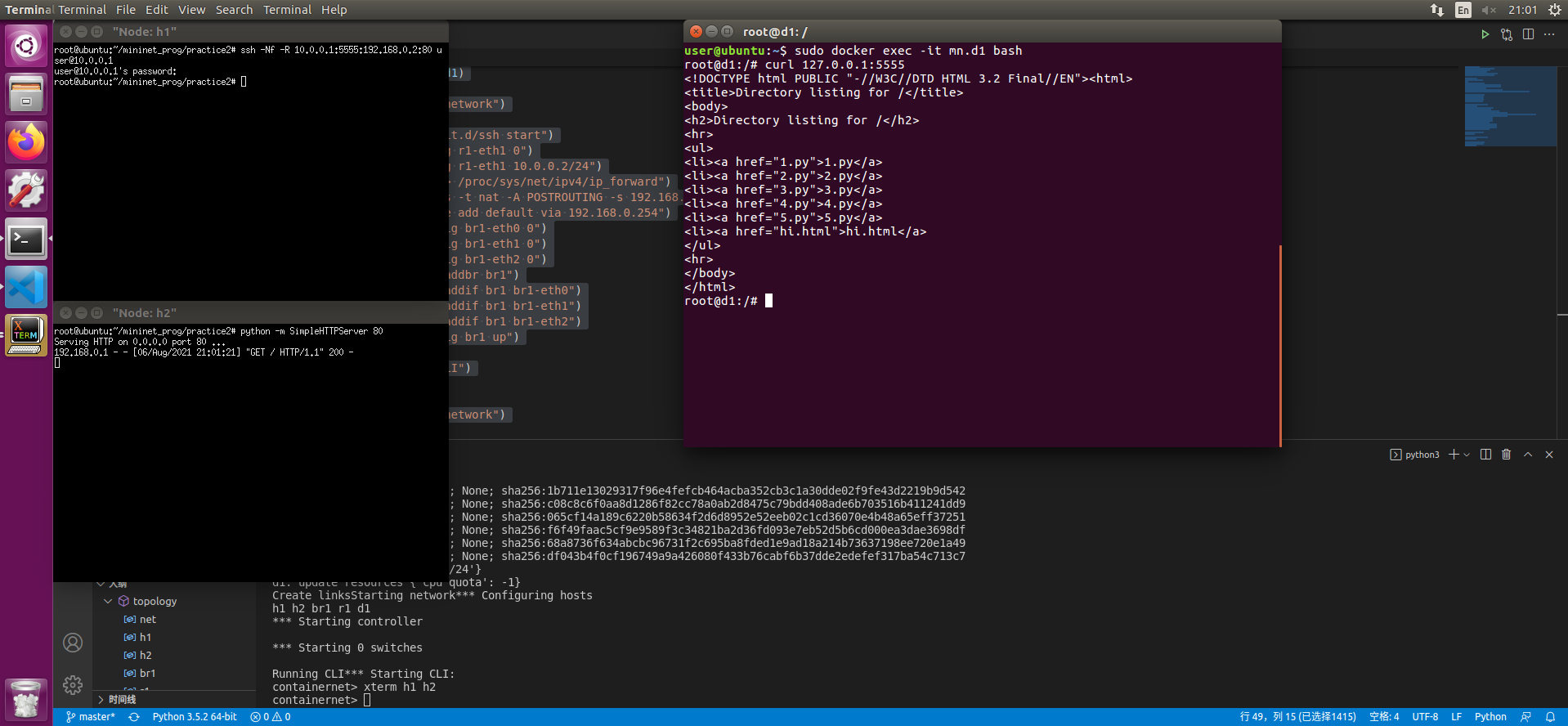
3. Dynamic Forwarding
拓扑结构如下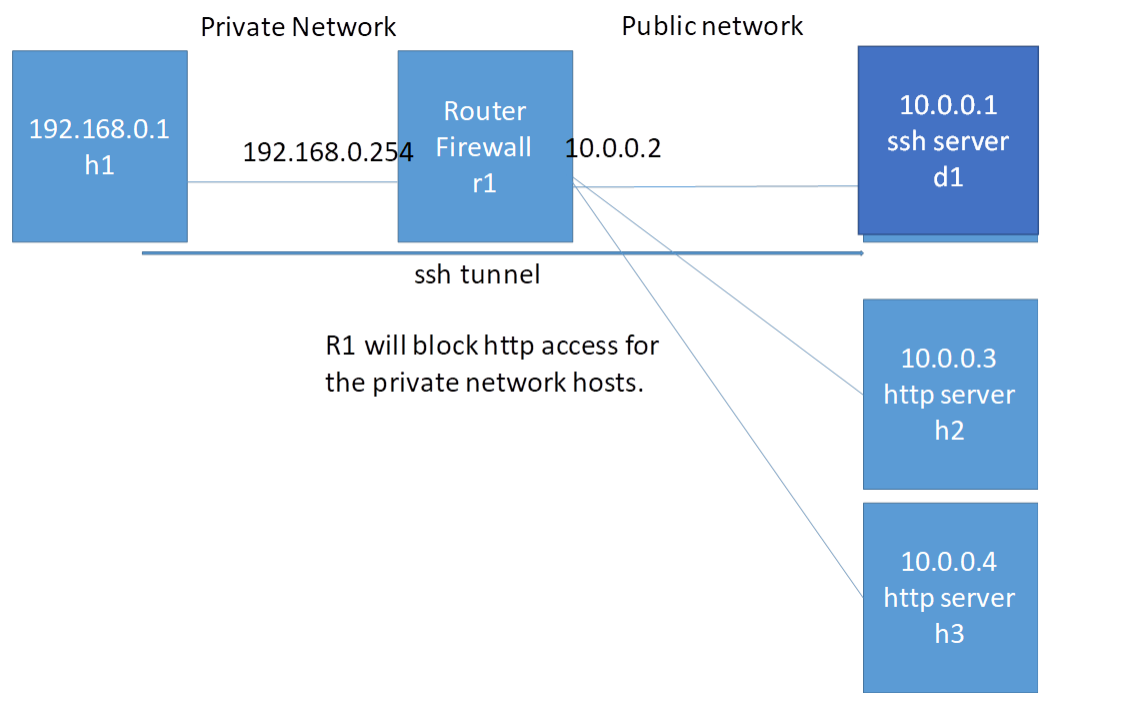
目标: 在这个拓扑中 r1阻止了对外网的80端口的访问 此时可以使用ssh完成对远程服务器80端口的存取
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54#!/user/bin/python
from mininet.net import Containernet
from mininet.node import Docker
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.log import setLogLevel,info
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link
def topology():
net=Containernet()
info("Adding hosts")
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='192.168.0.1/24')
r1=net.addHost('r1',ip='192.168.0.254/24')
d1=net.addDocker('d1',ip='10.0.0.1/24',dimage='smallko/php-apache-dev:v10')
br1=net.addHost('br1')
h2=net.addHost('h2',ip='10.0.0.3/24')
h3=net.addHost('h3',ip='10.0.0.4/24')
info("Create links")
net.addLink(h1,r1)
net.addLink(r1,br1)
net.addLink(d1,br1)
net.addLink(h2,br1)
net.addLink(h3,br1)
info("Starting network")
net.start()
d1.cmd("/etc/init.d/ssh start")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 0")
r1.cmd("ifconfig r1-eth1 10.0.0.2/24")
r1.cmd("echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward")
r1.cmd("iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -o r1-eth1 -j MASQUERADE")
r1.cmd("iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.0.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REJECT") # 阻止80端口访问
h1.cmd("ip route add default via 192.168.0.254")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth0 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth1 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth2 0")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1-eth3 0")
br1.cmd("brctl addbr br1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth0")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth1")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth2")
br1.cmd("brctl addif br1 br1-eth3")
br1.cmd("ifconfig br1 up")
info("Running CLI")
CLI(net)
info("Atopping network")
net.stop()
if __name__=="__main__":
setLogLevel('info')
topology()
准备一个网页hi.html1
2
3
4
5
6
<html>
<body>
<h1>Hi</h1>
</body>
</html>
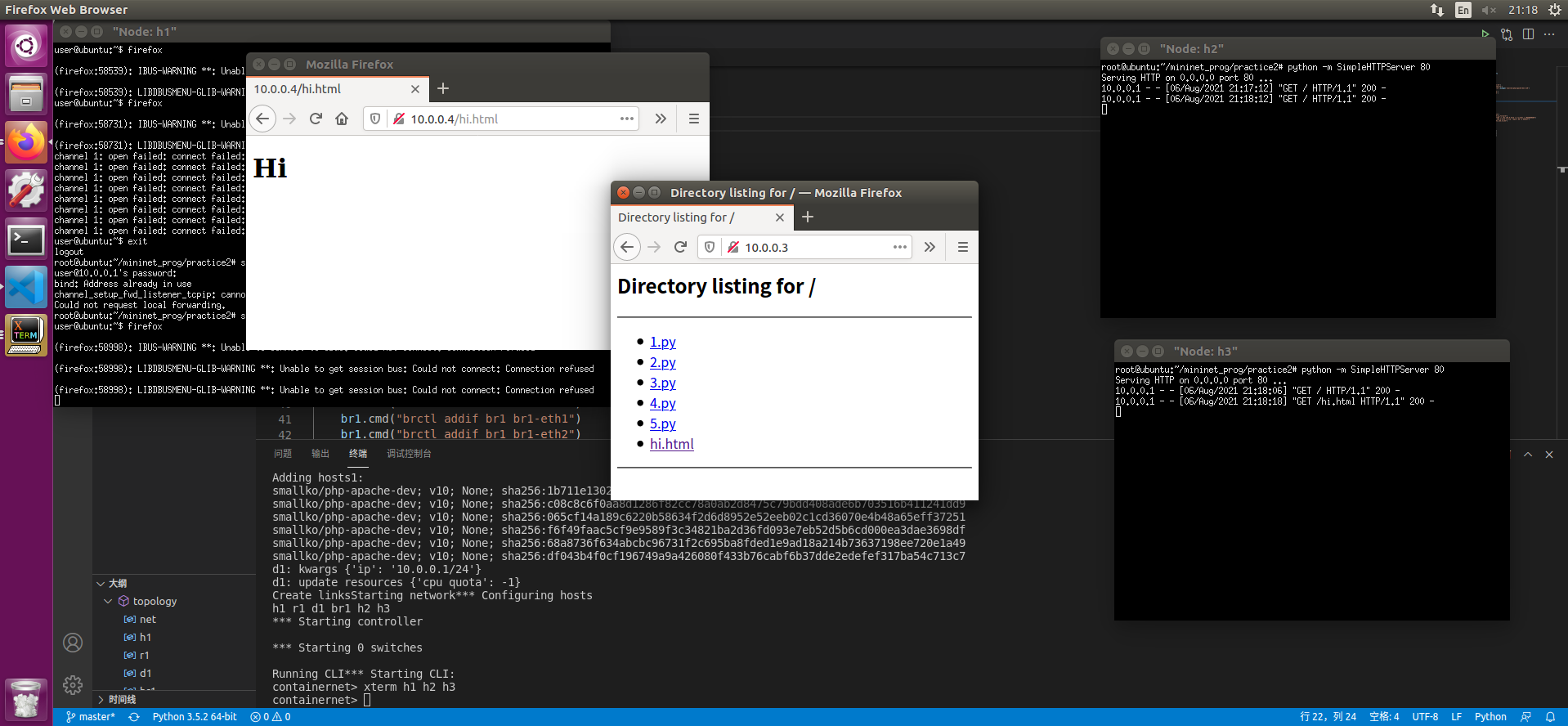
- 在CLI中输入xterm h1 h2 h3
- 在h2和还h3终端输入
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
此时尝试从h1 ping h2和h3 是可以ping通的
但是curl无法存取80端口的网页hi.html
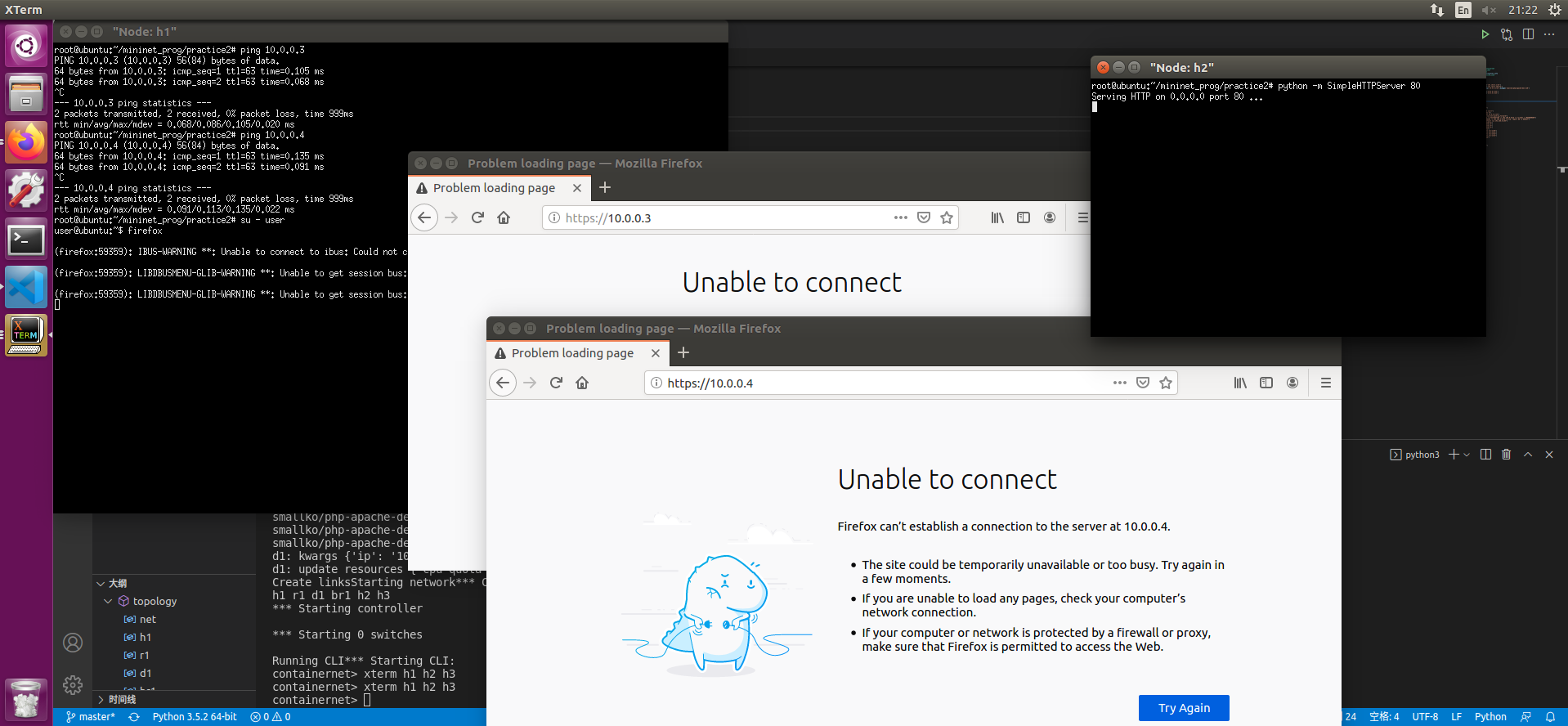
- 在h1终端中使用
ssh -Nf -D 127.0.0.1:8080 user@10.0.0.1输入密码 - 在h1终端中使用
su - user切换到普通用户 使用
firefox打开firefox 设置中设置SockV5代理为127.0.0.1 8080端口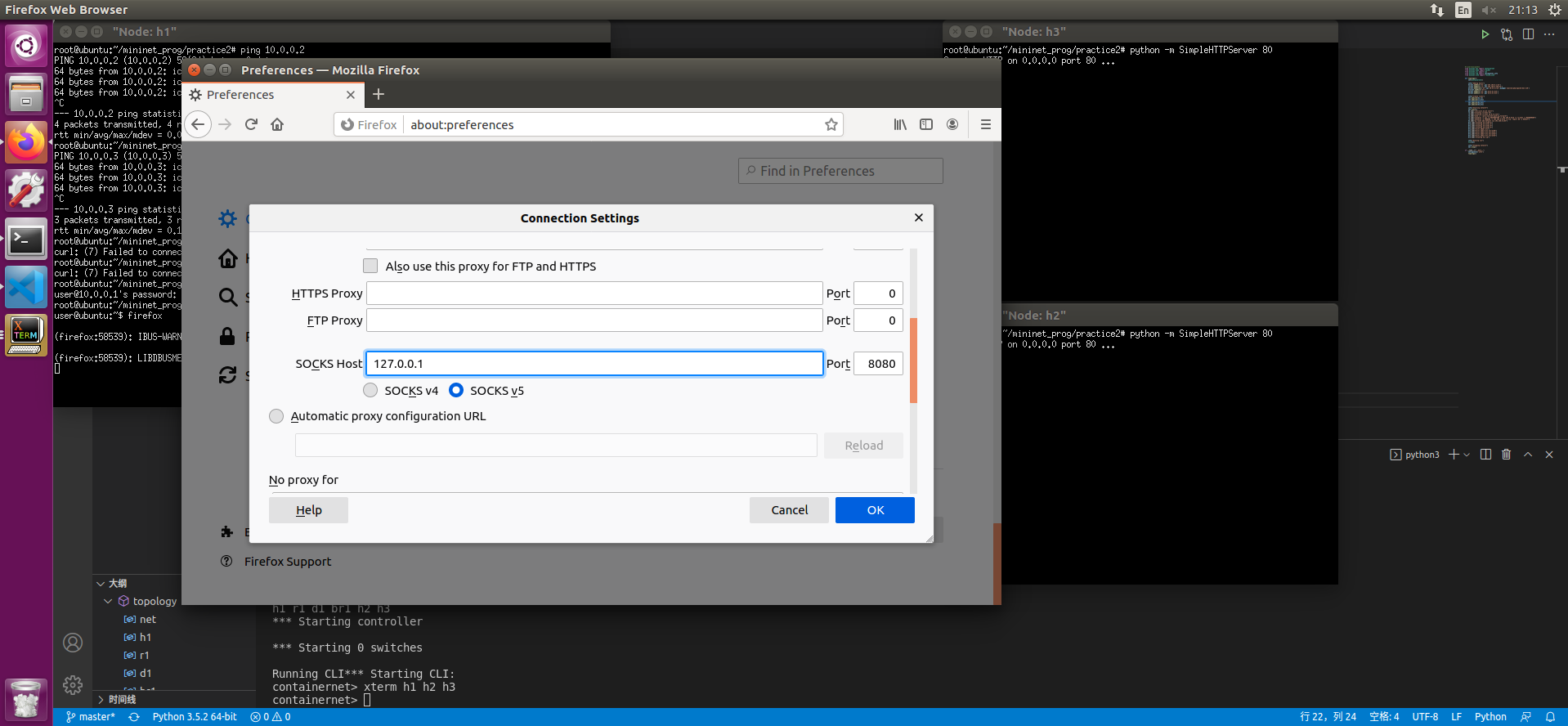
可以访问10.0.0.3和10.0.0.4的hi.html了
12. OVS的操作
实验所用拓扑结构: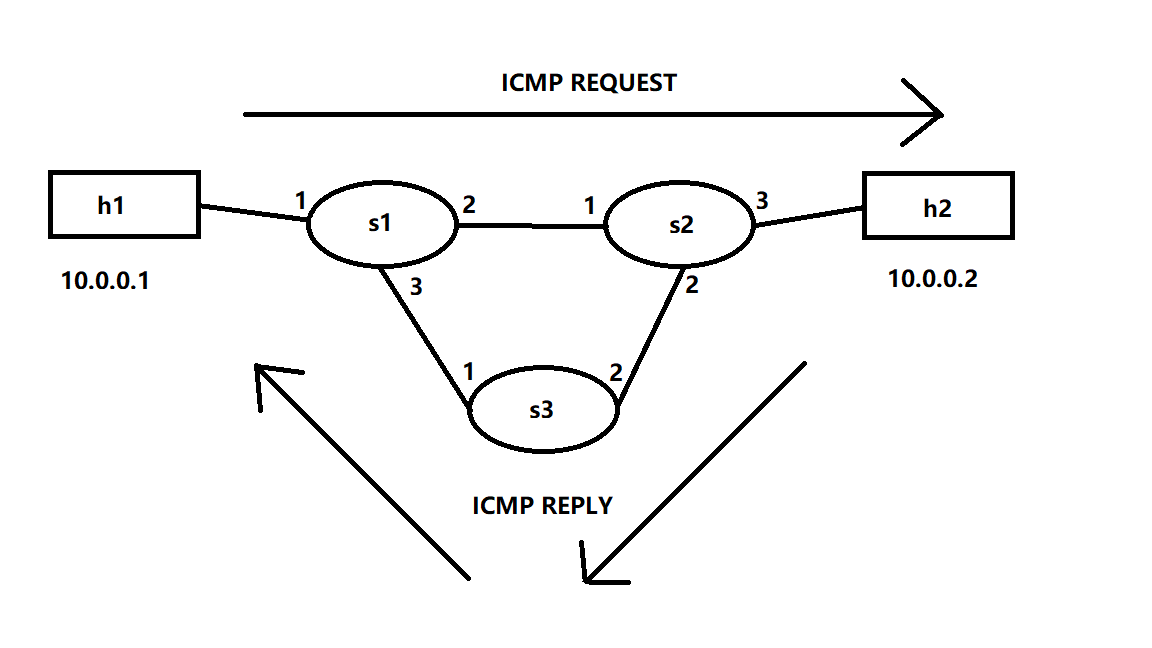
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29#!/usr/bin/env python
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.link import TCLink,Link,Intf
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.node import Controller,RemoteController
if "__main__" == __name__:
net=Mininet(link=TCLink)
h1=net.addHost("h1")
h2=net.addHost("h2")
s1=net.addSwitch('s1')
s2=net.addSwitch('s2')
s3=net.addSwitch('s3')
c0=net.addController('c0',controller=RemoteController)
net.addLink(h1,s1)
net.addLink(s1,s2)
net.addLink(s1,s3)
net.addLink(s3,s2)
net.addLink(s2,h2)
net.build()
c0.start()
s1.start([c0])
s2.start([c0])
s3.start([c0])
CLI(net)
net.stop()
然后我们通过命令行手动下发流表1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16# s1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 arp,arp_op=1,arp_spa=10.0.0.1,arp_tpa=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 arp,arp_op=1,arp_spa=10.0.0.2,arp_tpa=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 arp,arp_op=2,arp_spa=10.0.0.1,arp_tpa=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 arp,arp_op=2,arp_spa=10.0.0.2,arp_tpa=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 icmp,nw_src=10.0.0.1,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0,actions=output:2
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 icmp,nw_src=10.0.0.2,nw_dst=10.0.0.1,icmp_type=0,icmp_code=0,actions=output:1
# s2
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 arp,arp_op=1,arp_spa=10.0.0.1,arp_tpa=10.0.0.2,actions=output:3
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 arp,arp_op=1,arp_spa=10.0.0.2,arp_tpa=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 arp,arp_op=2,arp_spa=10.0.0.1,arp_tpa=10.0.0.2,actions=output:3
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 arp,arp_op=2,arp_spa=10.0.0.2,arp_tpa=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 icmp,nw_src=10.0.0.1,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,icmp_type=8,icmp_code=0,actions=output:3
ovs-ofctl add-flow s2 icmp,nw_src=10.0.0.2,nw_dst=10.0.0.1,icmp_type=0,icmp_code=0,actions=output:2
# s3
ovs-ofctl add-flow s3 icmp,nw_src=10.0.0.2,nw_dst=10.0.0.1,icmp_type=0,icmp_code=0,actions=output:1
此时h1可以ping通h2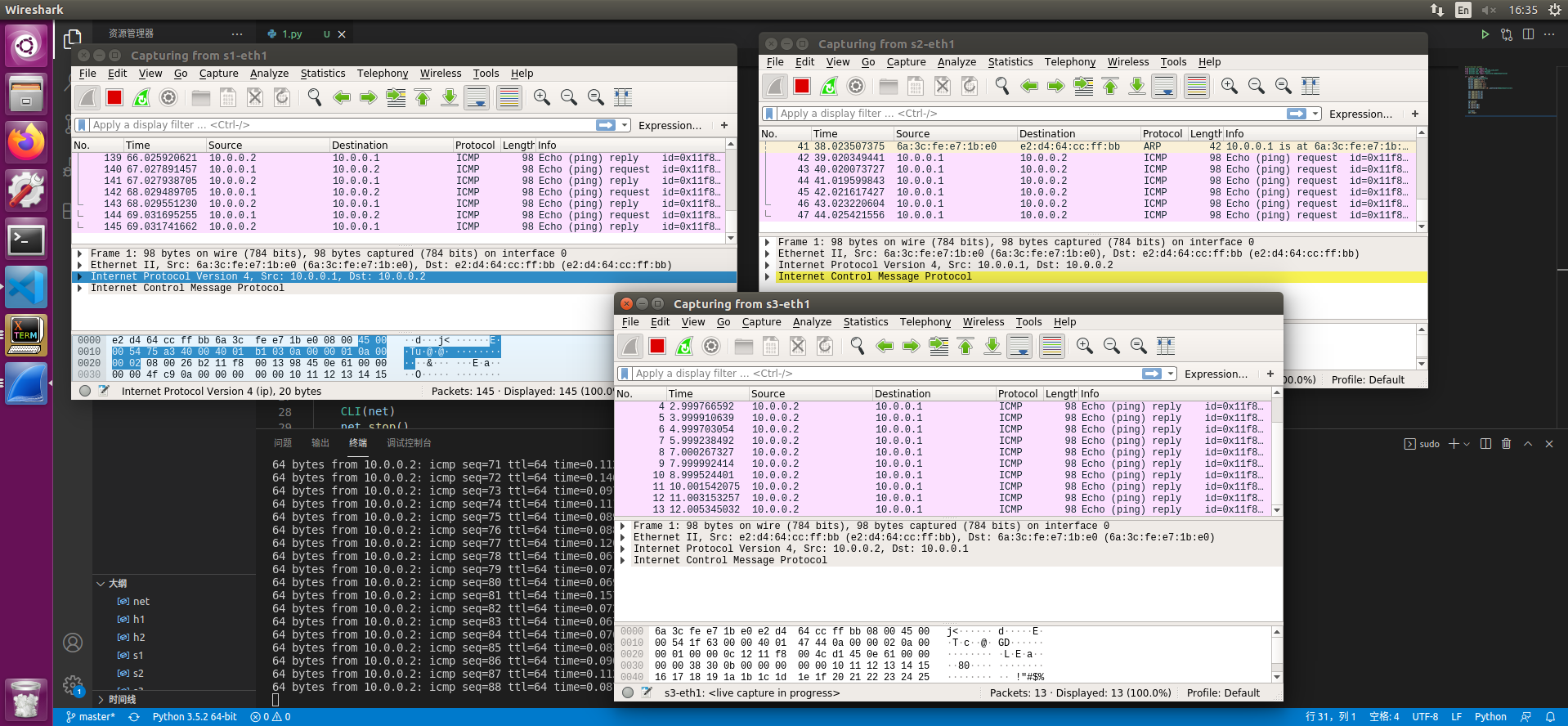
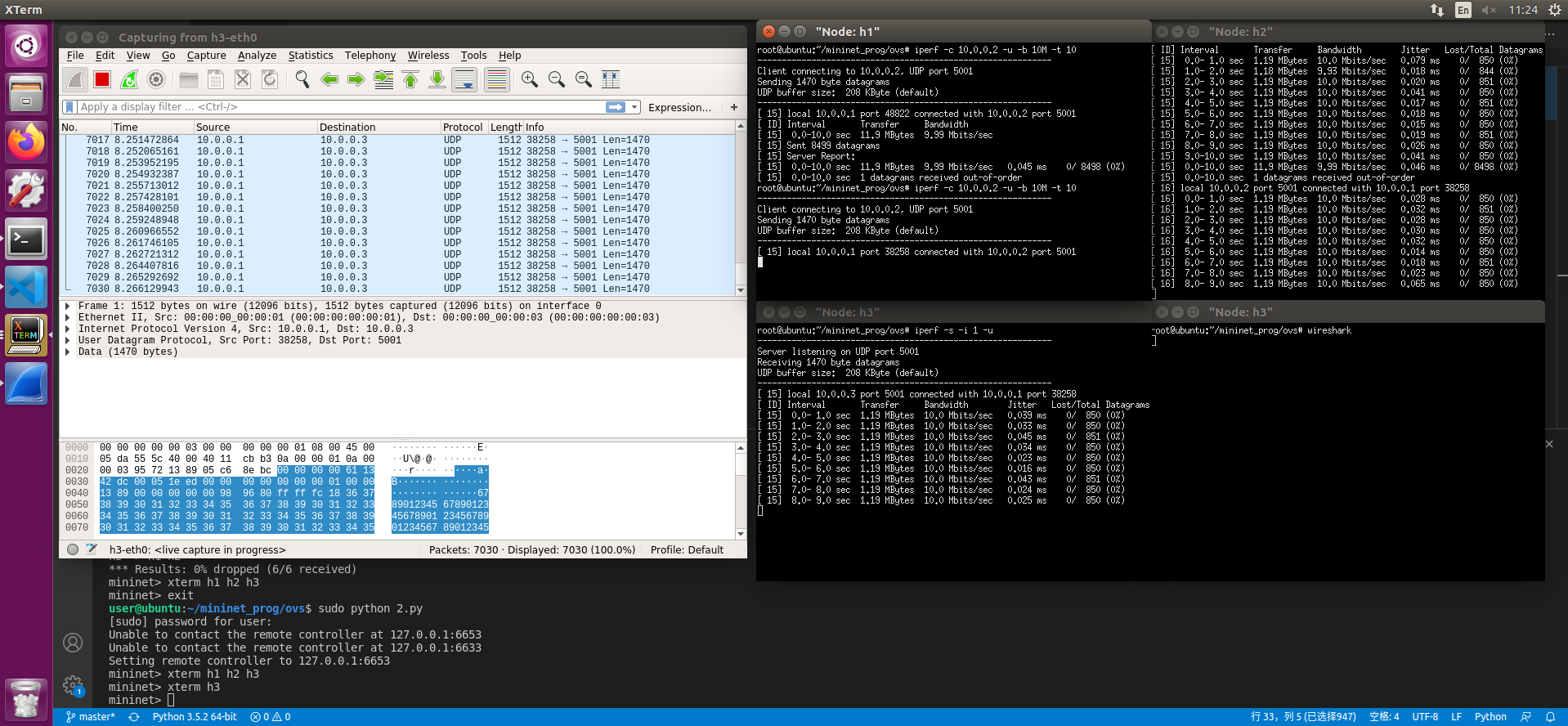
13. OVS交换机封包复制示例介绍
实验所用拓扑结构: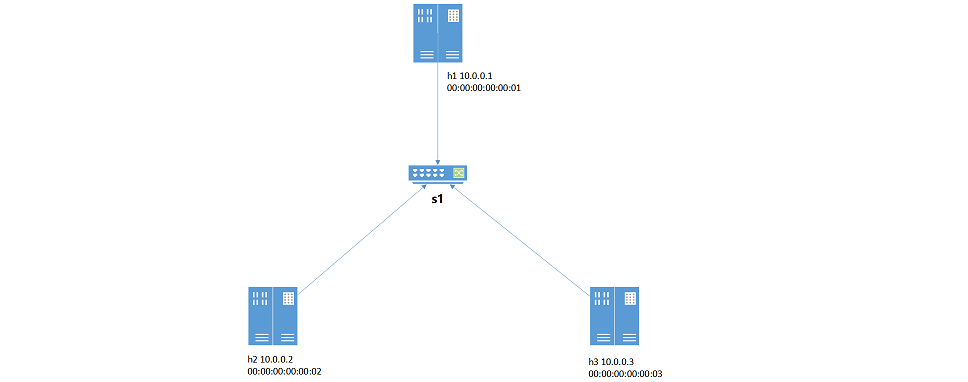
mininet脚本:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.link import Link,TCLink,Intf
from mininet.node import Controller,RemoteController
if '__main__'==__name__:
net=Mininet(link=TCLink)
h1=net.addHost('h1',ip='10.0.0.1/24',mac='00:00:00:00:00:01')
h2=net.addHost('h2',ip='10.0.0.2/24',mac='00:00:00:00:00:02')
h3=net.addHost('h3',ip='10.0.0.3/24',mac='00:00:00:00:00:03')
s1=net.addSwitch('s1')
c0=net.addController('c0',controller=RemoteController)
net.addLink(h1,s1)
net.addLink(h2,s1)
net.addLink(h3,s1)
net.build()
c0.start()
s1.start([c0])
h1.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.2 00:00:00:00:00:02")
h1.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.3 00:00:00:00:00:03")
h2.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.1 00:00:00:00:00:01")
h2.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.3 00:00:00:00:00:03")
h3.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.1 00:00:00:00:00:01")
h3.cmd("arp -s 10.0.0.2 00:00:00:00:00:02")
CLI(net)
net.stop()
实验目标:通过h1发往h2的udp数据包复制一份给h3
1. 直接复制 不修改信息
下发如下流表1
2
3
4ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 priority=1,ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.1,actions=output:1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 priority=1,ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 priority=1,ip,nw_dst=10.0.0.3,actions=output:3
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 priority=10,udp,nw_src=10.0.0.1,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2,output:3
此时 三台机器可以互相ping 且h1->h2的udp包会转发一份给h3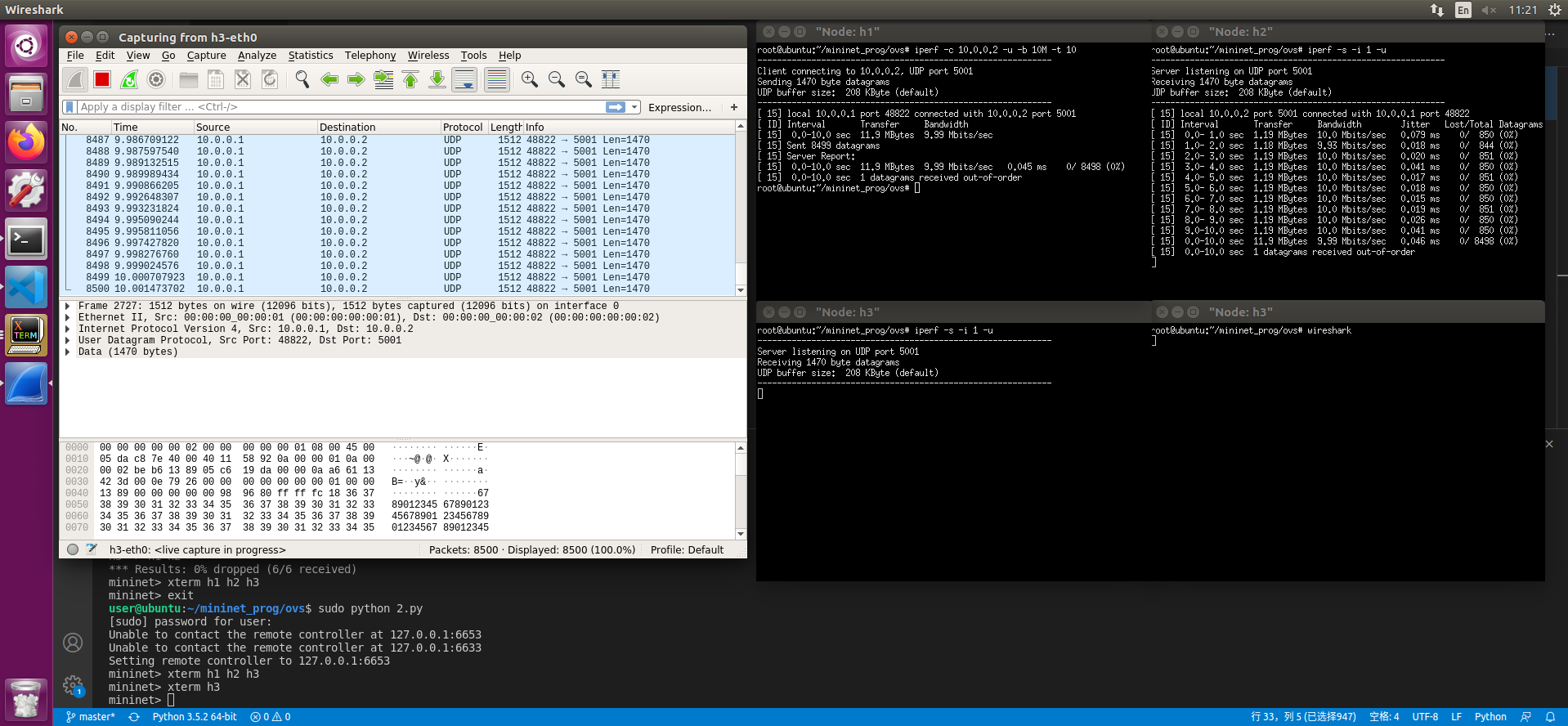
2. 复制并修改目的地址
在1的基础上下发如下流表1
ovs-ofctl add-flow s1 priority=100,udp,nw_src=10.0.0.1,nw_dst=10.0.0.2,actions=output:2,mod_dl_dst=00:00:00:00:00:03,mod_nw_dst=10.0.0.3,output:3
此时 h3会收到修改后的数据包