LeetCode87.扰乱字符串
题目描述
使用下面描述的算法可以扰乱字符串 s 得到字符串 t :
- 如果字符串的长度为 1 ,算法停止
- 如果字符串的长度 > 1 ,执行下述步骤:
- 在一个随机下标处将字符串分割成两个非空的子字符串。即,如果已知字符串 s ,则可以将其分成两个子字符串 x 和 y ,且满足 s = x + y 。
- 随机 决定是要「交换两个子字符串」还是要「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」。即,在执行这一步骤之后,s 可能是 s = x + y 或者 s = y + x 。
- 在 x 和 y 这两个子字符串上继续从步骤 1 开始递归执行此算法.
给你两个 长度相等 的字符串 s1 和 s2,判断 s2 是否是 s1 的扰乱字符串。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false .
示例
示例一1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11输入:s1 = "great", s2 = "rgeat"
输出:true
解释:s1 上可能发生的一种情形是:
"great" --> "gr/eat" // 在一个随机下标处分割得到两个子字符串
"gr/eat" --> "gr/eat" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」
"gr/eat" --> "g/r / e/at" // 在子字符串上递归执行此算法。两个子字符串分别在随机下标处进行一轮分割
"g/r / e/at" --> "r/g / e/at" // 随机决定:第一组「交换两个子字符串」,第二组「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」
"r/g / e/at" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 继续递归执行此算法,将 "at" 分割得到 "a/t"
"r/g / e/ a/t" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」
算法终止,结果字符串和 s2 相同,都是 "rgeat"
这是一种能够扰乱 s1 得到 s2 的情形,可以认为 s2 是 s1 的扰乱字符串,返回 true
示例二1
2输入:s1 = "abcde", s2 = "caebd"
输出:false
示例三1
2输入:s1 = "a", s2 = "a"
输出:true
思路与方法
显然 若s和t长度不同 则必不能由s变化为t
若长度相同 则存在一个分割点i1,使s分割为s1和s2,一个分割点i2,使t分割为t1和t2
满足
- 没交换 s1->t1 s2->t2
- 交换了 s2->t1 s1->t2
子问题
分别讨论两种情况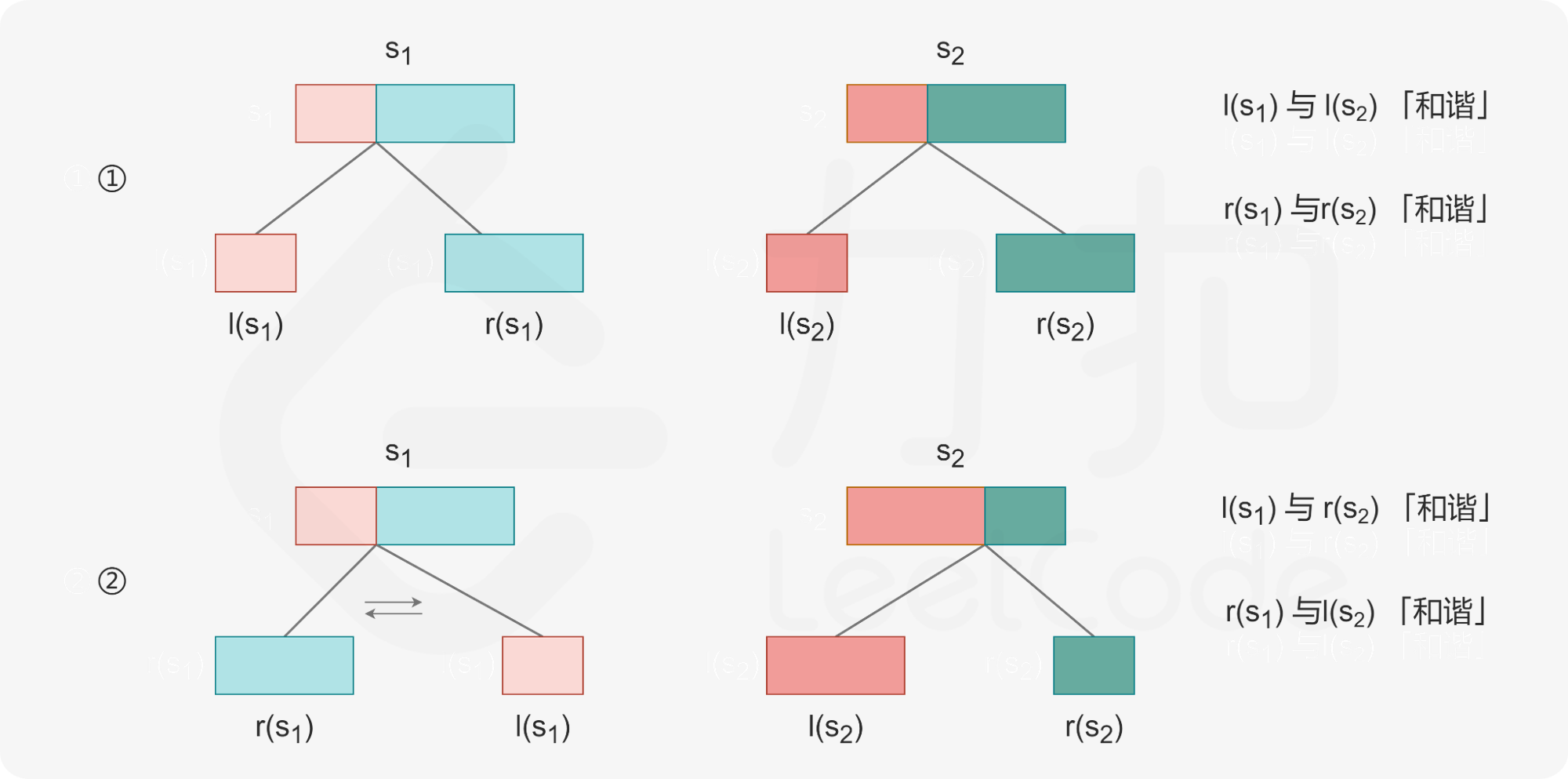
记忆化搜索数组
可先设记忆化搜索数组为mem[i][j][k][h]
又因为s和t长度的关系 j-i=h-k
则可将数组降低为三维 mem[i][j][l]
表示从字符串 s 中 i 开始长度为 l 的字符串是否能变换为从字符串 t 中 j 开始长度为 l 的字符串
状态转移方程
初始条件
对于长度为1的串 只有相等才能变换得到 相等为 true 不相等为 false
代码
1 | class Solution { |