Unix-Linux编程实践1-who命令的实现
介绍
在使用Unix/Linux系统时,常常需要知道有哪些用户正在使用系统,系统是否繁忙,为了回答这些问题,所有的多用户系统都会有这个命令
关于who
我们将通过三个问题的解答来学习who命令
who能做什么
Unix/Linux who命令用于显示系统中有哪些使用者正在上面,显示的资料包含了使用者 ID、使用的终端机、从哪边连上来的、上线时间、呆滞时间、CPU 使用量、动作等等。
使用权限:所有使用者都可使用。

who是如何工作的
通过命令man who可以打开who的帮助文档
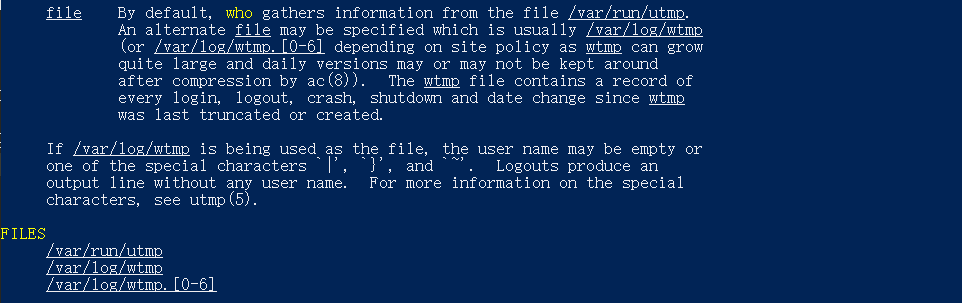
从上文易知 已登陆用户信息存储在/var/run/utmp中,who通过读取该文件来获得信息
通过man utmp可以获得utmp文件记录的数据结构信息
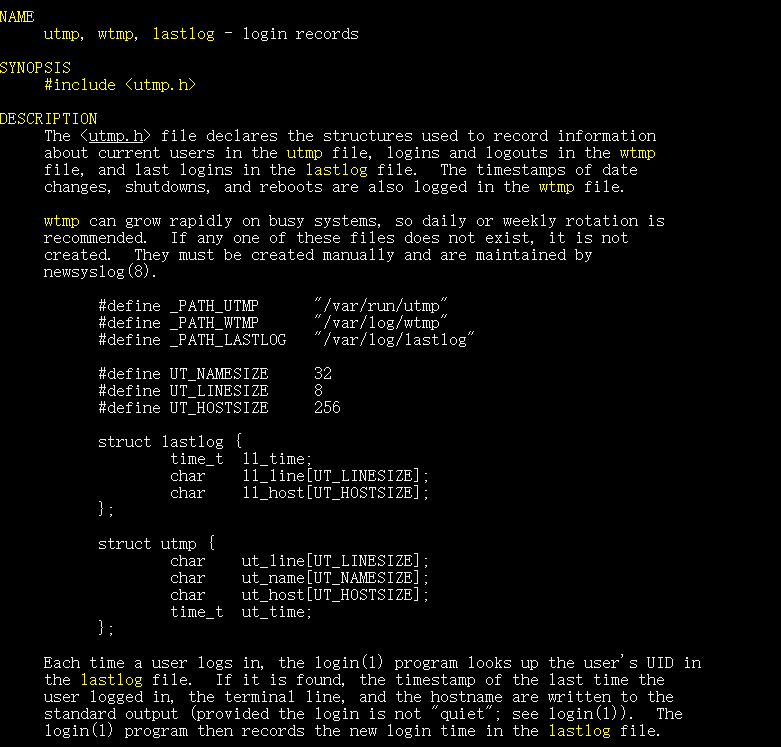
所以who的工作原理可用以下流程完成
如何编写who
如何读取文件
通过搜索和read和file有关的文档
可以找到open(2)
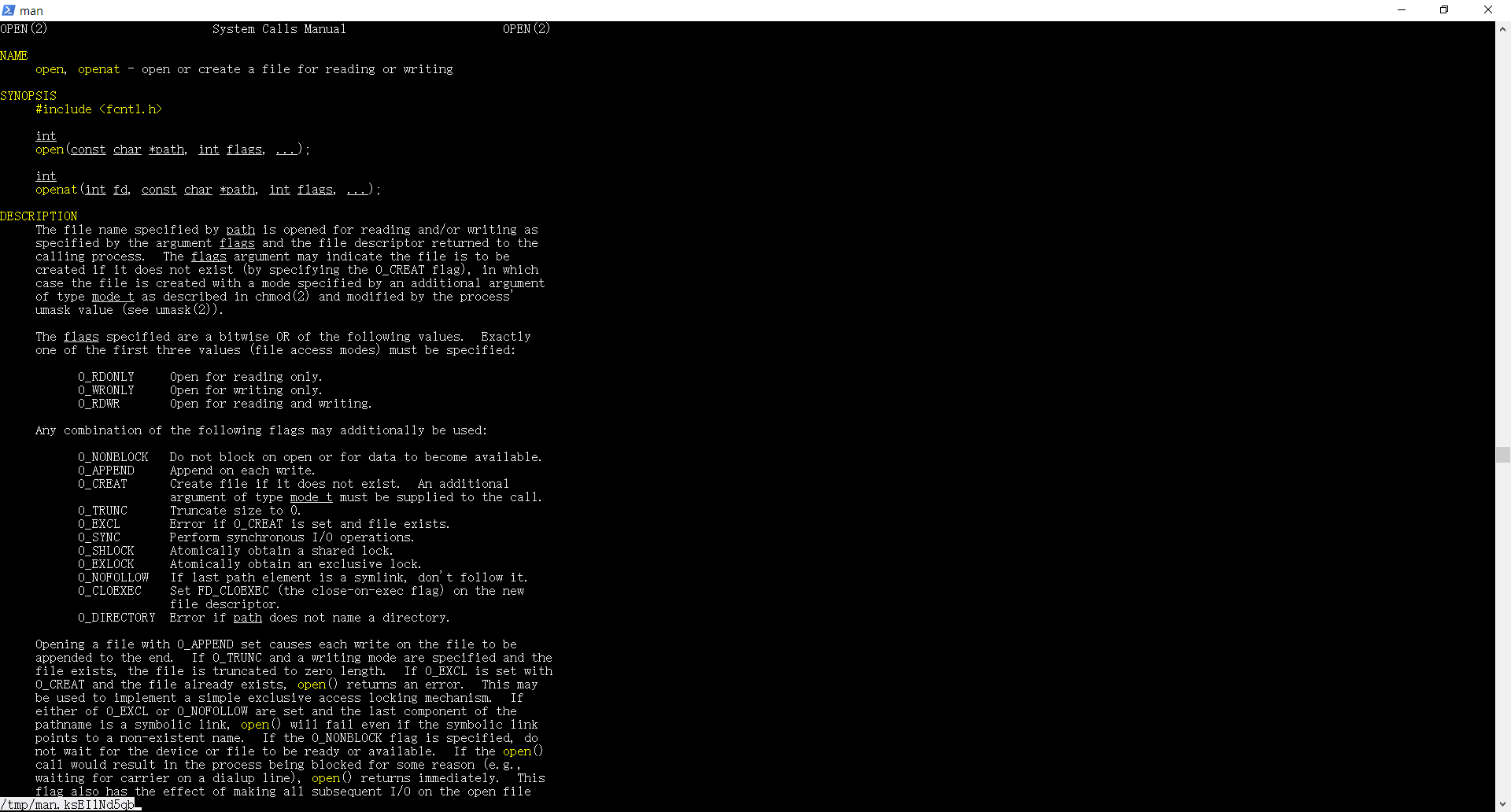
通过open的文档可以找到其他的函数,分别是read close
open在打开文件时需要提供打开方式
| open |
|
| target |
打开文件 |
| header |
#include <fcntl.h> |
| definition |
int fd = open(const char *name,int flags) |
| arguments |
name:文件名,flags:读取模式 |
| ret |
-1 error,int success |
其中 flags可以为O_RDONLY O_WRONLY O_RDWR
| read |
|
| target |
读取文件 |
| header |
#include <unistd.h> |
| definition |
ssize_t numread = read(int fd,void *buf,size_t qty) |
| arguments |
fd:文件描述符,buf:缓冲区,qty:读取数量 |
| ret |
-1 error,numread success |
| close |
|
| target |
关闭文件 |
| header |
#include <unistd.h> |
| definition |
int result = close(int fd) |
| arguments |
fd:文件描述符 |
| ret |
-1 error,0 success |
编写who1.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SHOW_HOSTS
void show_info(struct utmp *utmpbuf);
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct utmp rec;
int utmpfd;
int reclen=sizeof(rec);
utmpfd=open(_PATH_UTMP,O_RDONLY);
if(utmpfd==-1){
perror(_PATH_UTMP);
exit(1);
}
while(read(utmpfd,&rec,reclen) == reclen){
show_info(&rec);
}
close(utmpfd);
return 0;
}
void show_info(struct utmp *utmpbuf){
printf("%-8.8s",utmpbuf->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s",utmpbuf->ut_line);
printf(" ");
printf("%10ld",(long)utmpbuf->ut_time);
printf(" ");
#ifdef SHOW_HOSTS
printf("(%s)",utmpbuf->ut_host);
#endif
printf("\n");
}
|
编译who1
cc who1.c -o who1
执行
./who1
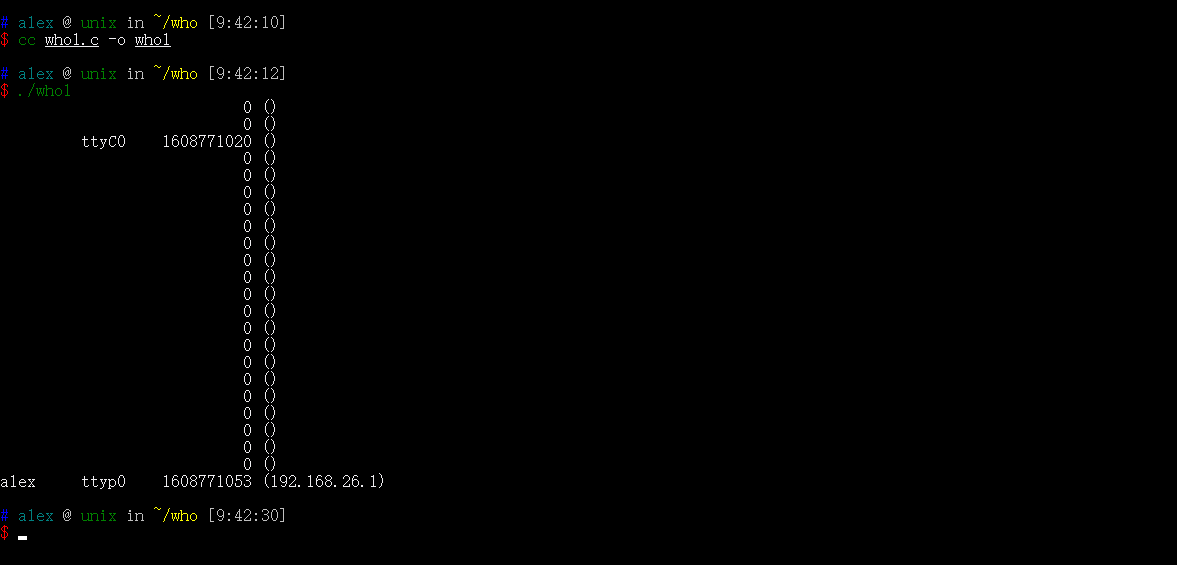

可见 who1已经可以工作了,但是仍有很多可以完善
编写who2.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SHOW_HOSTS
void show_info(struct utmp *utmpbuf);
void show_time(time_t time);
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
struct utmp rec;
int utmpfd;
int reclen=sizeof(rec);
utmpfd=open(_PATH_UTMP,O_RDONLY);
if(utmpfd==-1){
perror(_PATH_UTMP);
exit(1);
}
while(read(utmpfd,&rec,reclen) == reclen){
show_info(&rec);
}
close(utmpfd);
return 0;
}
void show_info(struct utmp *utmpbuf){
if(strlen(utmpbuf->ut_name)==0) return;
printf("%-8.8s",utmpbuf->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s",utmpbuf->ut_line);
printf(" ");
show_time(utmpbuf->ut_time);
printf(" ");
#ifdef SHOW_HOSTS
printf("(%s)",utmpbuf->ut_host);
#endif
printf("\n");
}
void show_time(time_t time){
char *str=ctime(&time);
printf("%12.12s",str+4);
}
|
编译并运行
cc who2.c -o who2&&./who2
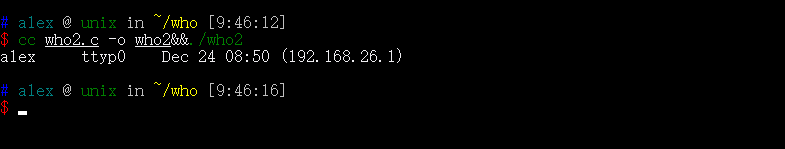
此时who已经可以按要求正常运行了
who1.c
who2.c






